-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7.6k
Async Operators
The operators described on this page are part of the Async class and are used to convert synchronous methods into Observables.
-
start( )— create an Observable that emits the return value of a function -
toAsync( )orasyncAction( )orasyncFunc( )— convert a function or Action into an Observable that executes the function and emits its return value -
startFuture( )— convert a function that returns Future into an Observable that emits that Future's return value -
deferFuture( )— convert a Future that returns an Observable into an Observable, but do not attempt to get the Observable that the Future returns until an Observer subscribes -
fromCancellableFuture( ),startCancellableFuture( ), anddeferCancellableFuture( )— versions of Future-to-Observable converters that monitor the subscription status of the Observable to determine whether to halt work on the Future -
forEachFuture( )— pass observer methods to an Observable but also have it behave like a Future that blocks until it completes -
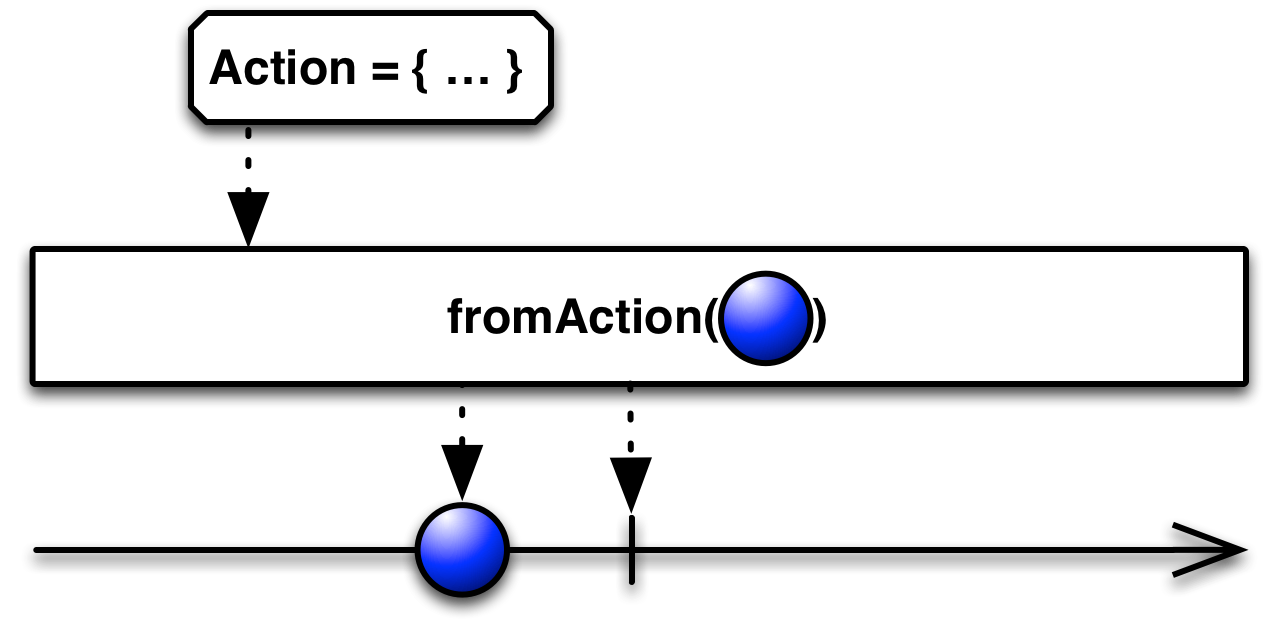
fromAction( )— convert an Action into an Observable that invokes the action and emits its result when an observer subscribes -
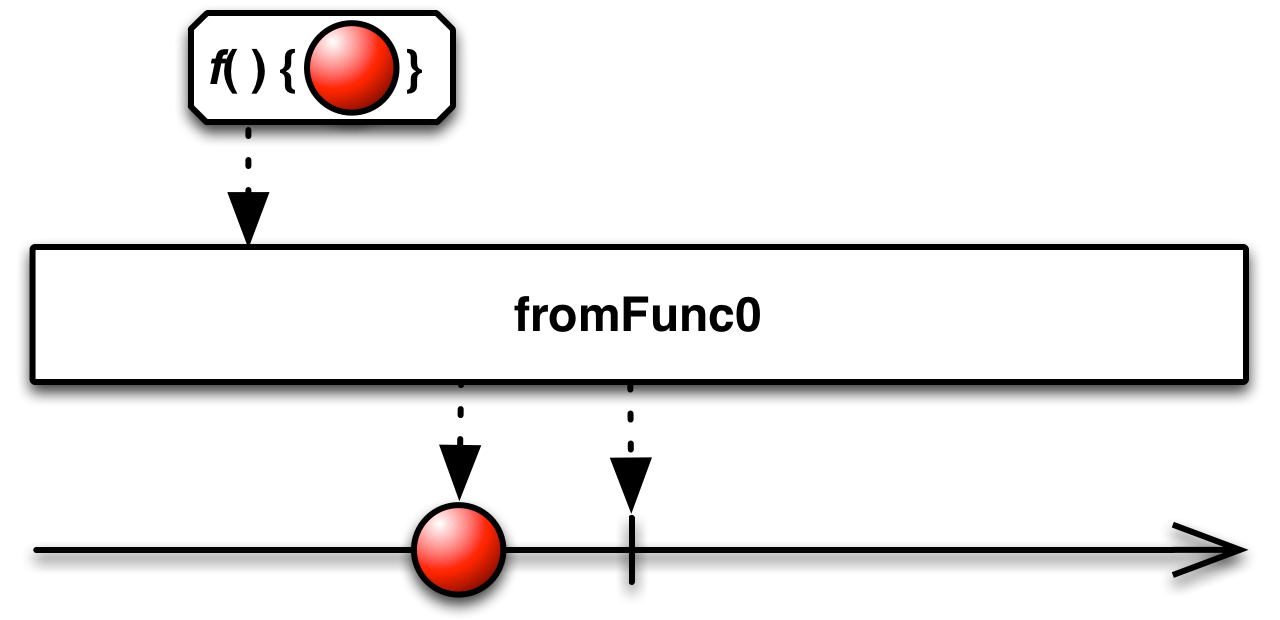
fromFunc0( )— convert a Func0 into an Observable that invokes the function and emits its result when an observer subscribes -
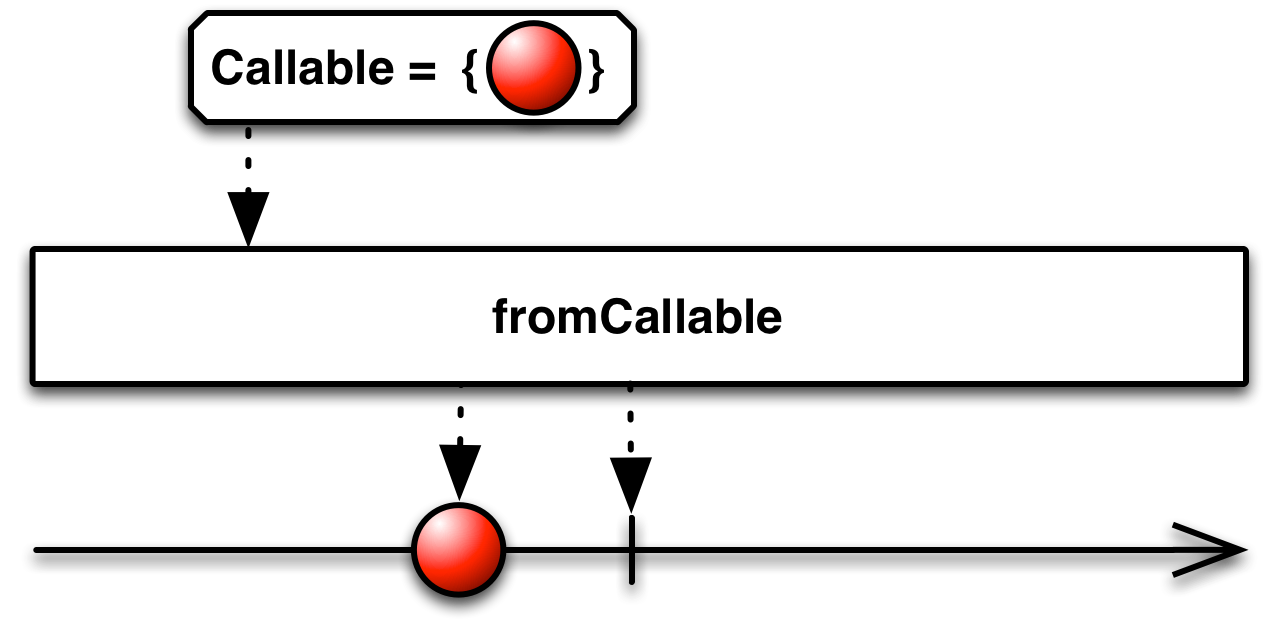
fromCallable( )— convert a Callable into an Observable that invokes the callable and emits its result or exception when an observer subscribes -
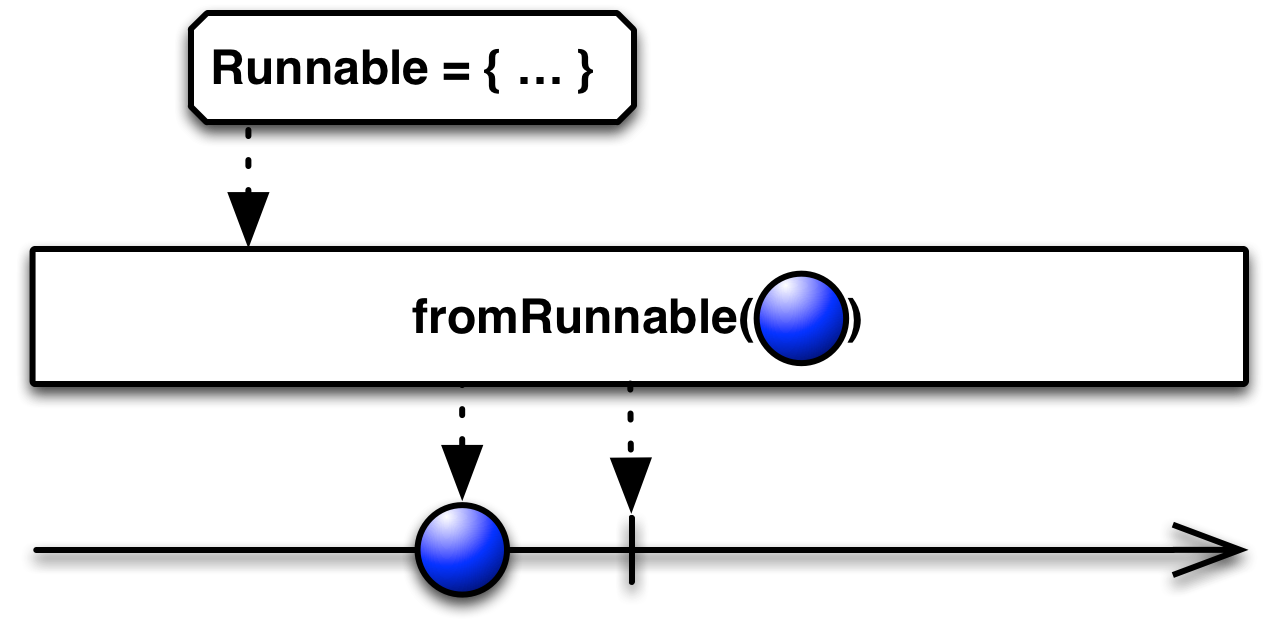
fromRunnable( )— convert a Runnable into an Observable that invokes the runable and emits its result when an observer subscribes
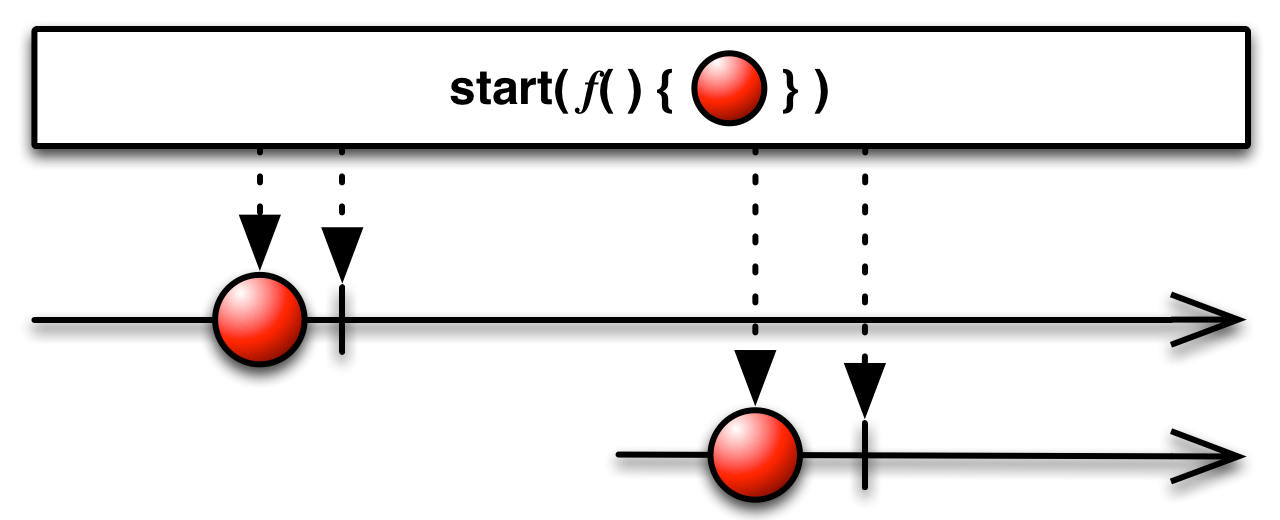
Pass the start( ) method a function that returns a value, and start( ) will execute that function asynchronously and return an Observable that will emit that value to any subsequent Observers.
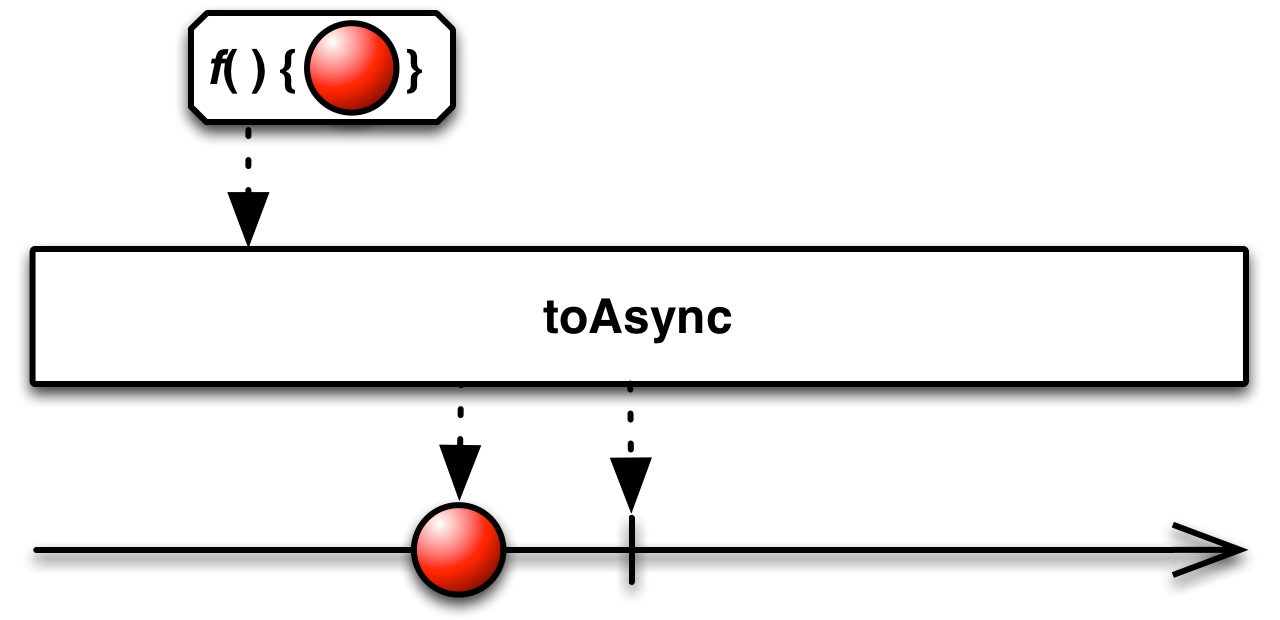
With toAsync( ) you can create an Observable that, when it is subscribed to, executes a function (or Action) of your choosing and emits its return value before completing. In the case of an Action, it will emit null before completing. Note that even if the resulting Observable is subscribed to more than once, the function will only be executed once, and its sole return value will be emitted to all future observers.
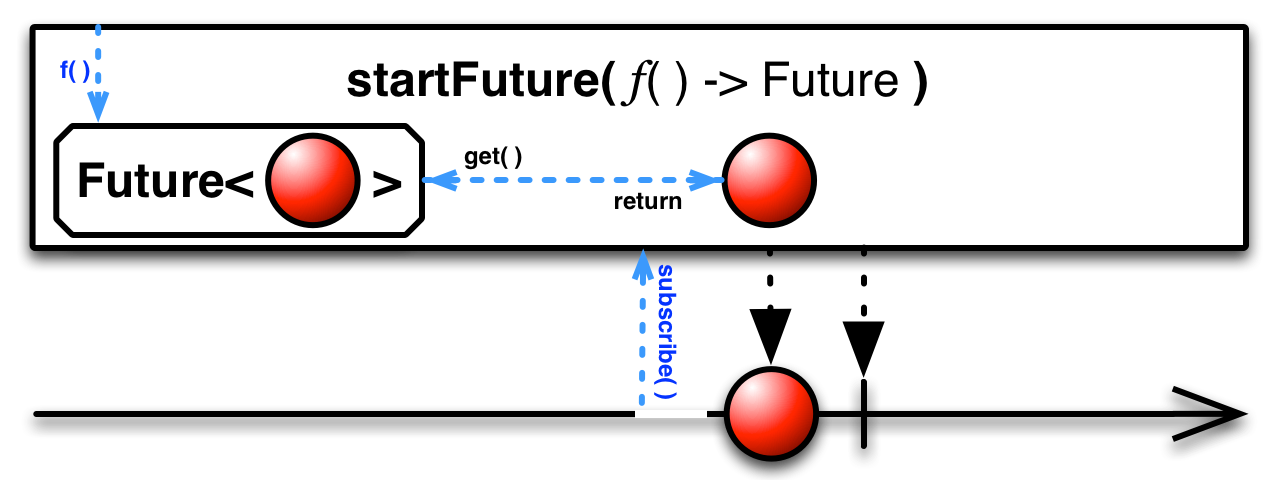
The startFuture( ) method is similar to the fromFuture( ) method except that it calls the function to obtain the Future immediately, and attempts to get its value even before an Observer subscribes to the resulting Observable. It then holds this value and returns it to any future observer.
convert a Future that returns an Observable into an Observable, but do not attempt to get the Observable that the Future returns until an Observer subscribes
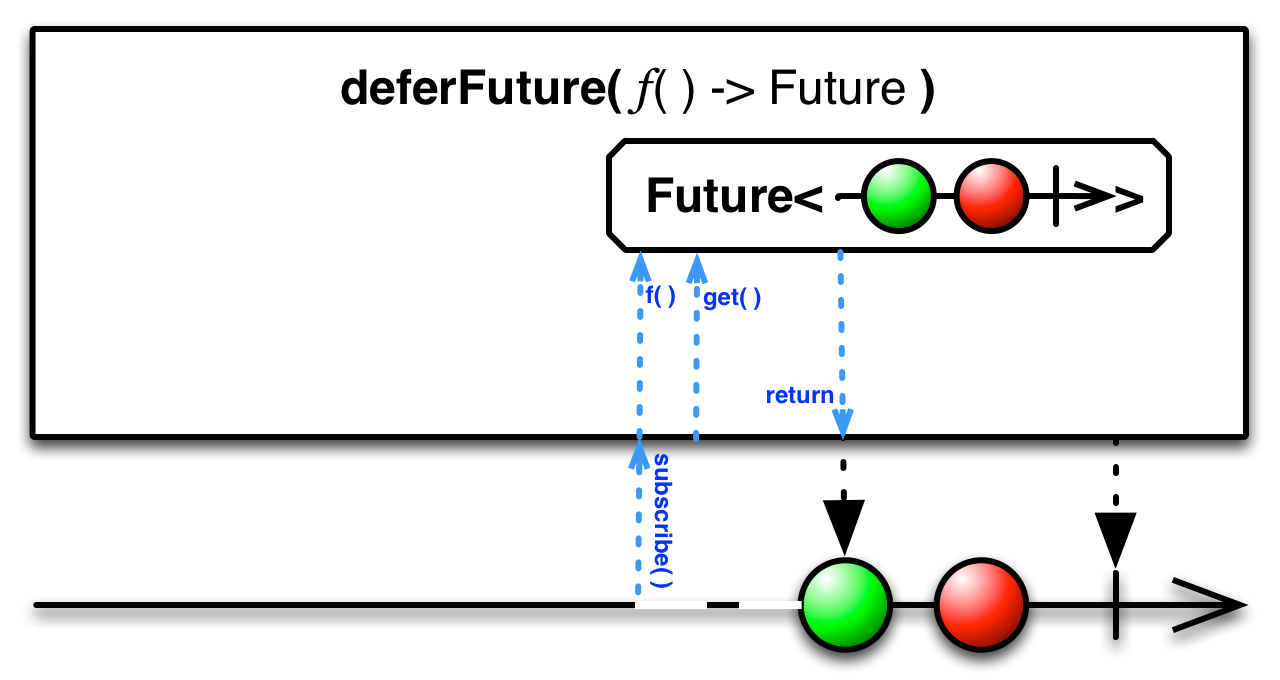
You can use the deferFuture( ) operator to convert a Future that returns an Observable into an Observable that emits the values of that returned Observable in such a way that the Future is not invoked until an observer subscribes to the resulting Observable.
versions of Future-to-Observable converters that monitor the subscription status of the Observable to determine whether to halt work on the Future
If the a subscriber to the Observable that results when a Future is converted to an Observable later unsubscribes from that Observable, it can be useful to have the ability to stop attempting to retrieve items from the Future. The "cancellable" Future enables you do do this. These three methods will return Observables that, when unsubscribed to, will also "unsubscribe" from the underlying Futures.
pass observer methods to an Observable but also have it behave like a Future that blocks until it completes
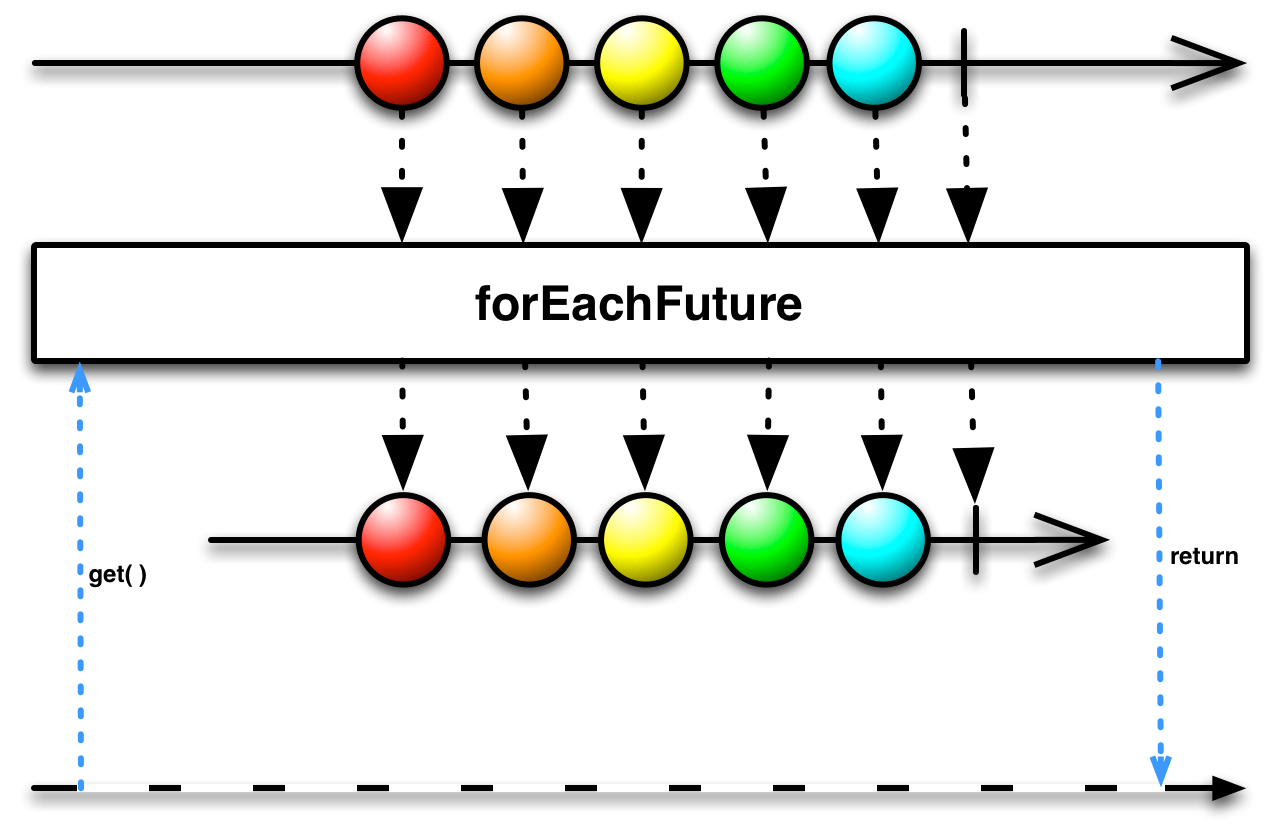
You pass forEachFuture( ) some subset of observer methods (onNext, onError, and onCompleted) and the Observable will call them in the usual way. But forEachFuture( ) itself returns a Future that blocks until the source Observable completes, and then returns either the completion or the error, depending on how the Observable completed.
convert an Action into an Observable that invokes the action and emits its result when an observer subscribes
convert a Func0 into an Observable that invokes the function and emits its result when an observer subscribes
convert a Callable into an Observable that invokes the callable and emits its result or exception when an observer subscribes
convert a Runnable into an Observable that invokes the runable and emits its result when an observer subscribes
Copyright (c) 2016-present, RxJava Contributors.
Twitter @RxJava | Gitter @RxJava