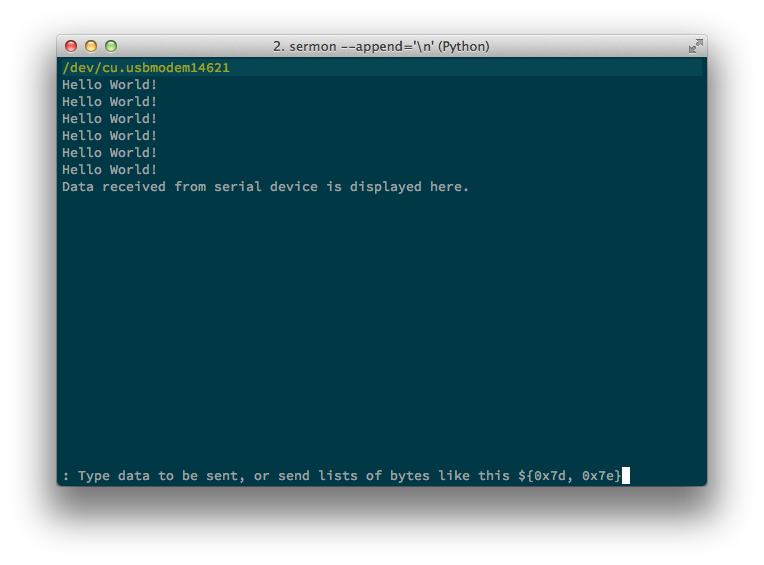
A command line serial monitor and transmitter written in python for use in POSIX systems. Sermon performs the same function as the Arduino Serial Monitor, but is available on the command line, and offers some additional capabilities like the ability to send lists of raw bytes, data from files, and can log received data to a file.
Install python, install pip, then:
$ pip install sermon
If you are on a Mac you can also use homebrew:
$ brew tap dbridges/formula
$ brew install sermon
List available serial devices:
$ sermon -l
/dev/cu.Bluetooth-Incoming-device
/dev/cu.Bluetooth-Modem
/dev/cu.usbserial-A601EI5P
Connect to a serial device with a baud rate of 115200 kbps:
$ sermon --baud=115200 /dev/tty.usbserial-A601EI5P
If a device is not specified Sermon queries the user to select an available device.
$ sermon
1. /dev/tty.Bluetooth-Incoming-device
2. /dev/tty.Bluetooth-Modem
3. /dev/tty.usbserial-A601EI5P
Select desired device [1-3]:
Raw bytes can be sent using the ${0x48, 0x44, ...} syntax. This syntax is available at the prompt as well as in any options given. Numbers greater than 255 are truncated to their least significant bits.
$ sermon --frame='${0x7E}' # Frame boundaries used in HDLC
Once connected to a device, type text at the prompt, then press enter to send. Received data will automatically be displayed in the top window.
Similar to IPython, Sermon employs a limited set of magic commands to access certain useful functions at the prompt.
%help, %h
Display help.
%about, %a
Display information about Sermon.
%exit, %quit, %q
Exit Sermon.
%send [FILE], %s [FILE]
Send the contents of the given file to the connected serial device.
%logstart [FILE], %ls [FILE]
Start logging all received data to the given file.
%logon, %lo
Resume logging after a %logoff. %logstart must be called prior to using %logoff or %logon.
%logoff, %lf
Temporarily stop logging. Logging can be resumed using %logon.
%clear, %c
Clear the received data window.
%version, %v
Display the current version.
usage: sermon [-h] [-v] [-l] [-b BAUD] [--append APPEND]
[--frame FRAME] [--bytesize {5,6,7,8}]
[--parity {even,none,space,odd,mark}]
[--stopbits {1,1.5,2}] [--xonxoff] [--rtscts]
[--dsrdtr]
[device]
Monitors specified serial device.
positional arguments:
device Device name or path.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version Show version.
-l, --list List available serial devices.
-b BAUD, --baud BAUD Baudrate, defaults to 115200.
--append APPEND Append given string to every command.
--frame FRAME Frame command with given string.
--bytesize {5,6,7,8} Number of data bits, defaults to 8.
--parity {even,none,space,odd,mark}
Enable parity checking, defaults to none.
--stopbits {1,1.5,2} Number of stop bits, defaults to 1.
--xonxoff Enable software flow control.
--rtscts Enable hardware (RTS/CTS) flow control.
--dsrdtr Enable hardware (DSR/DTR) flow control.
append
Useful if you want to append newlines to each data packet, sermon --append='\n'
frame
Surrounds command with the given string, useful for communicating to devices which are expecting frame boundaries. If --append and --frame are used together any strings given with --append are appended first, then the resulting string is surround by the string given in the --frame option. If you are implementing HDLC protocol this could be useful: sermon --frame='${0x7E}'