A recommendation engine is a tool that predicts what a user will like among a list of items.
A simple recommendation engine has four parts:
- a set of users
- a set of items (e.g. videos)
- ratings that join users and items (e.g. thumbs on YouTube)
- a program that maps this information to predictions (AKA recommendations) of what items a user will like.
Our program is based on the assumption that users have similar preferences, i.e. one user liking an item means similar users will probably like that item too.
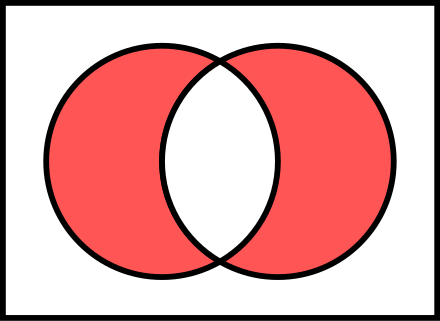
To determine which users are similar, it's helpful to think about the intersection and symmetric difference of preference sets.
intersection: the set comprised of items that appear in both input sets.
E.g. [1,2,3] n [1,3,4] -> [1,3]
symmetric difference: the set comprised of items that appear in only one of the input sets.
E.g. [1,2,3] ∆ [1,3,5] -> [2,5]
Similarity: A user is similar if they have more in common than not.
We can represent this by looking at the number of elements in the intersection of two users' preferences over the total items those users have rated, or
A n B / A u B
A more advanced concept is that users who disagree about an item (e.g. a likes 1, b dislikes 1) are more dissimilar than those who do not (e.g. a likes 1, b likes 2).
Once you determine a users' similarity, you can look for items your target user has not yet rated, and see if similar users liked that item.
Recommendations: An list of items, ordered such that the item with the greatest probability of being liked is first.
Generating a list of recommendations is straightfoward:
- getting a list of items the target user has not yet rated
- predicting the probability the target user will like each item
- sorting the resulting items by greatest probability of being liked first.
Sources: http://www.toptal.com/algorithms/predicting-likes-inside-a-simple-recommendation-engine