Evolving Deep Reinforcement Learning Agents through Advanced Information Processing Strategies: U-Net Layers & Frame Merging
Keywords: Deep Reinforcement Learning, Deep Q-Learning, Deep Convolutional Neural Networks, U-Net, Frame Merging, Information Processing, Computer Vision, OpenAI Gym, Keras, Python
Name: GoodOnions
Components: Daniele Cipollone, Federico Bono
This study examines the impact of input preprocessing techniques on the learning efficiency of Reinforcement Learning (RL) agents, with a specific focus on addressing the research question: ”How does the agent’s performance change when the environment is presented using a more dense representation (i.e., more information encoded in the same space or the same amount of information encoded in a smaller space)?” The research centers on integrating advanced image processing and dimensionality reduction strategies to enhance RL algorithm performance.
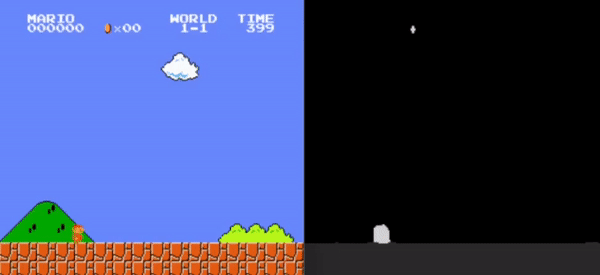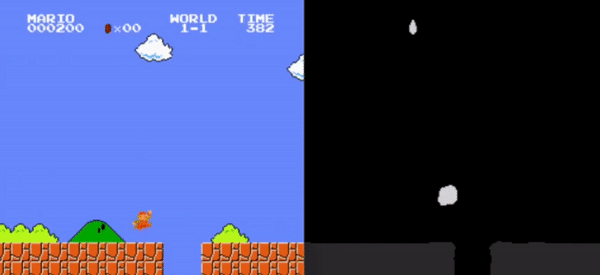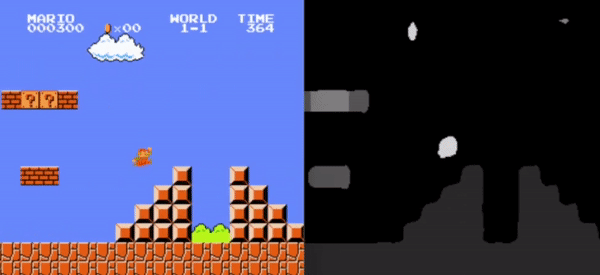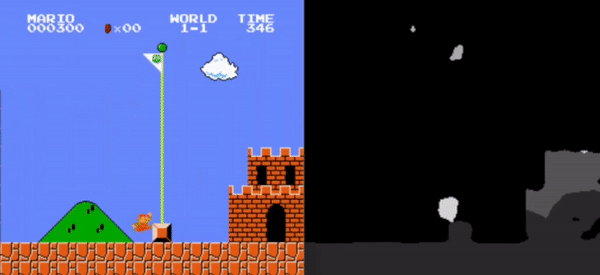
Utilizing the OpenAI Gym framework and the Super Mario video game environment, the study assesses the effectiveness of increasing information density provided to the agent, achieved through both the utilization of more data and the reduction of the input representation space. Key techniques explored encompass semantic segmentation with U-Net and its representation layers, as well as the development and application of a frame merging technique.
While neither method conclusively demonstrated an improvement in the agent’s performance, frame merging, which introduces the state-transition concept into the input representation, showcased a more stable enhancement in the agent’s capabilities.