Deterministic and Nondeterministic Finite State Machines for JavaScript. The backend for my regex library.
State Machines may be installed on node.js via the node package manager using the command npm install statemachines.
You may also install it on RingoJS using the command ringo-admin install aaditmshah/statemachines.
You may install it as a component for web apps using the command component install aaditmshah/statemachines.
A StateMachine is a pattern recognizer. There are two types of state machines - Deterministic and Nondeterministic. Both are equally powerful.
Deterministic state machines are faster. However nondeterministic state machines are easier to create. Fortunately there's a way to create an equivalent deterministic state machine from a nondeterministic one.
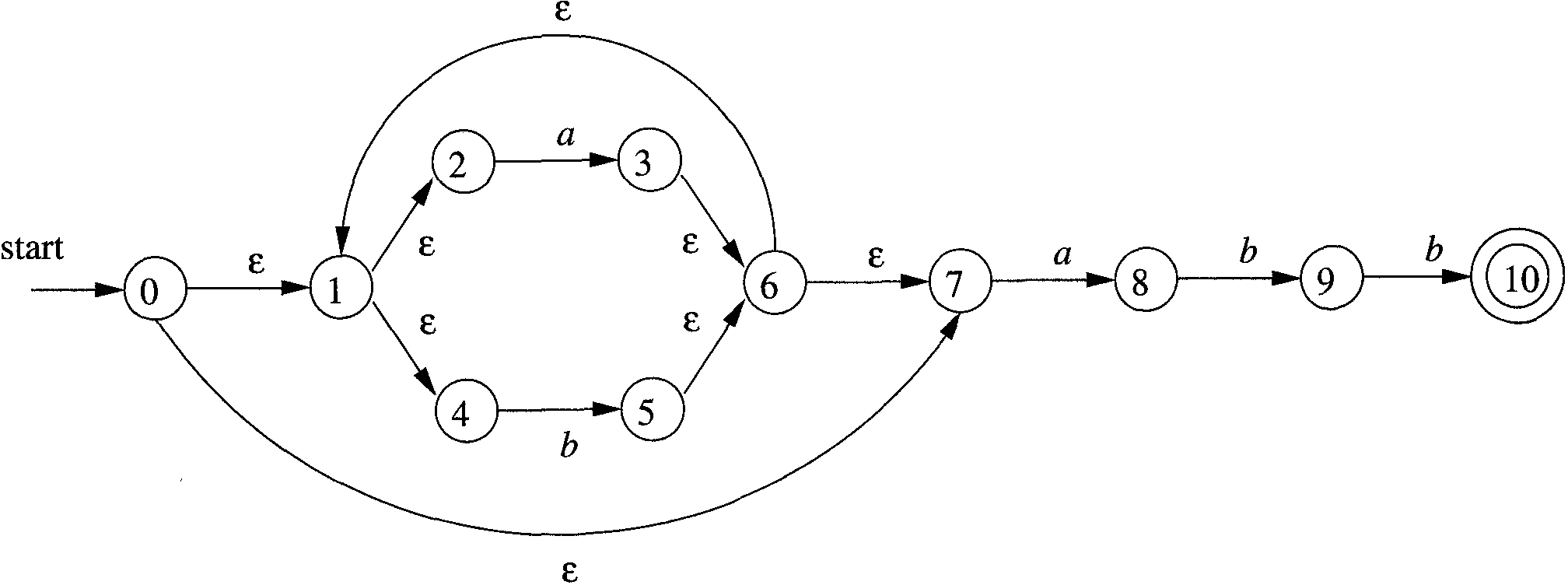
Consider the following nondeterministic state machine:
We construct it in JavaScript as follows:
var StateMachine = require("statemachines");
var nfa = new StateMachine.Nondeterministic([
{ "" : [1, 7] },
{ "" : [2, 4] },
{ "a": [3] },
{ "" : [6] },
{ "b": [5] },
{ "" : [6] },
{ "" : [1, 7] },
{ "a": [8] },
{ "b": [9] },
{ "b": [10] },
{ }
], [10]);The first parameter to StateMachine.Nondeterministic must be the transition table for the nondeterministic state machine. The second parameter must be list of final or accepting states of the state machine.
The state machine may now be used to test input strings as follows:
nfa.test("abb"); // true
nfa.test("aabb"); // true
nfa.test("babb"); // true
nfa.test("aaabb"); // true
nfa.test("ababb"); // true
nfa.test("abba"); // false
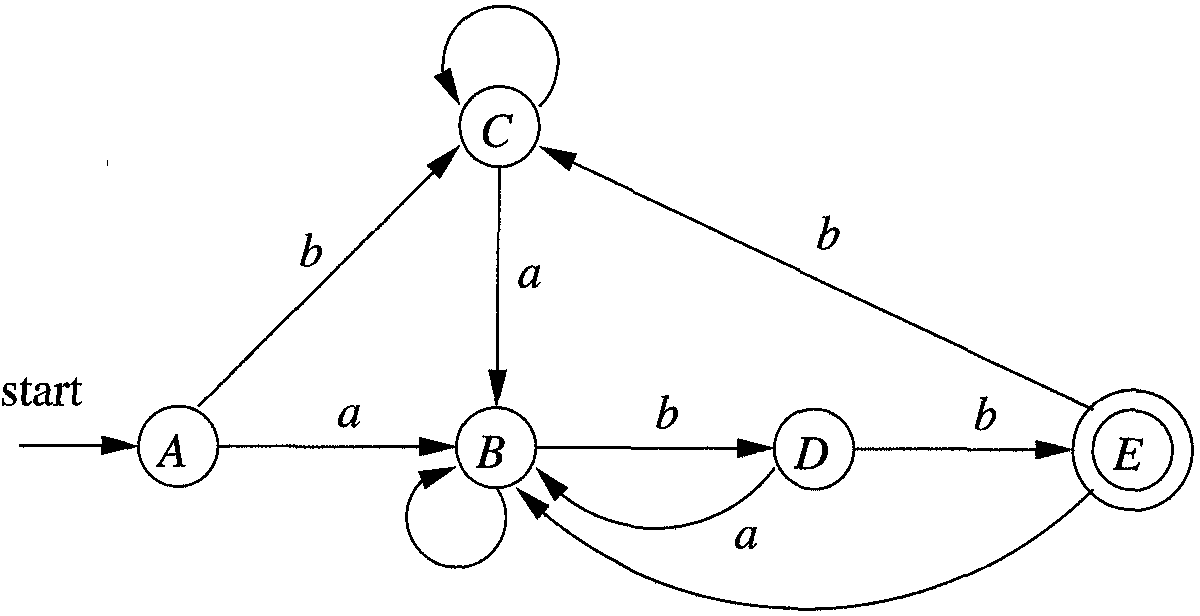
nfa.test("cabb"); // falseThe following deterministic state machine is equivalent to the above nondeterministic state machine:
We can construct it in JavaScript as follows:
var dfa = new StateMachine.Deterministic([
{
"a": 1,
"b": 2
},
{
"a": 1,
"b": 3
},
{
"a": 1,
"b": 2
},
{
"a": 1,
"b": 4
},
{
"a": 1,
"b": 2
}
], [4]);However it's more convenient to construct it from the nondeterministic state machine using the subset method:
var dfa = nfa.subset();The resulting deterministic state machine accepts the same language as the nondeterministic state machine:
dfa.test("abb"); // true
dfa.test("aabb"); // true
dfa.test("babb"); // true
dfa.test("aaabb"); // true
dfa.test("ababb"); // true
dfa.test("abba"); // false
dfa.test("cabb"); // falseThat's all folks.