-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 134
ReGrid File Storage
ReGrid is a distributed large file storage on top of RethinkDB. ReGrid is similarly inspired by GridFS from MongoDB. With ReGrid, a large 4GB file can be broken up into chunks and stored on a RethinkDB cluster. Later, the file can be retrieved by streaming the file back to the client. The figure below shows ReGrid storing a large video file in chunks across a three node cluster.
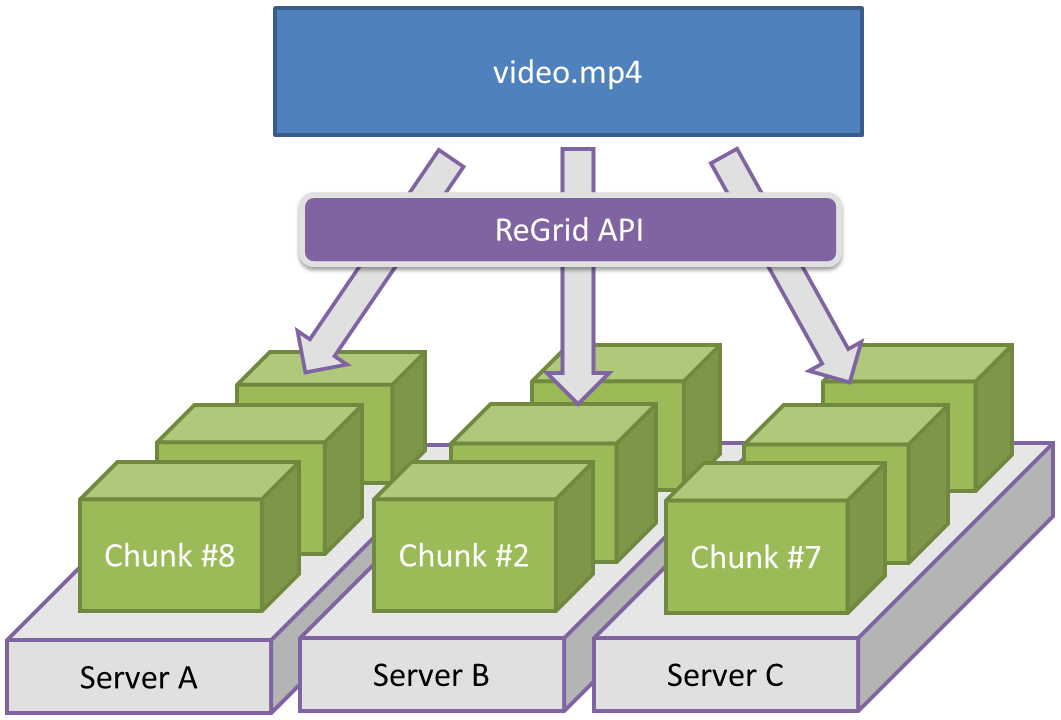 (Note: Please ask before using figures in presentations, videos, or other works. Thanks.)
(Note: Please ask before using figures in presentations, videos, or other works. Thanks.)
- Physical view refers to the low-level view of the physical topology, location, and layout of raw file data.
- Logical view refers to the high-level view of the file system's organization of files regardless of the physical layout of data.
NuGet Package RethinkDb.Driver.ReGrid
Install-Package RethinkDb.Driver.ReGridA Bucket is a logical set of files organized together. File read/download and write/upload operations are performed using a Bucket.
- A Bucket requires a RethinkDB database.
- A RethinkDB database can be partitioned into several Buckets.
- Multiple Buckets in the same RethinkDB database are differentiated by a Bucket's name.
- The default name for a Bucket is
fs.
The figure below illustrates the logical separation of buckets within a single MyFiles database:
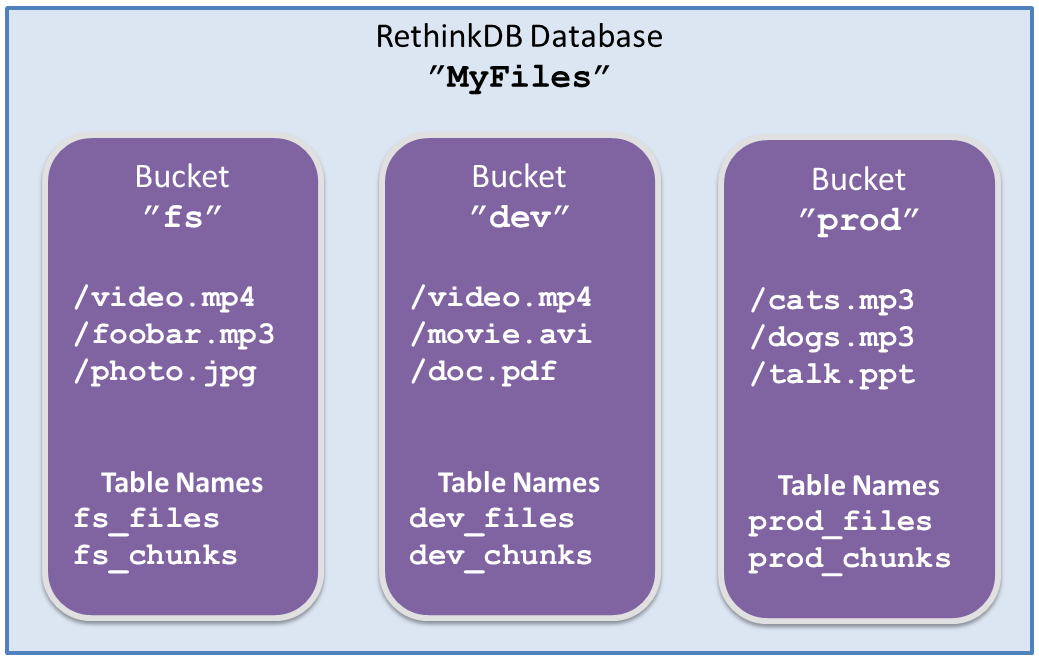
In Figure 2 above, there are three logical file Bucket stores in the MyFiles RethinkDB database. It is important to note that video.mp4 from the fs bucket is not the same file as video.mp4 from the dev bucket. Buckets can be used to organize files in any way app developers see fit.
To create a Bucket named dev in MyFiles simply:
var bucket = new Bucket(conn, "MyFiles", bucketName: "dev" );
bucket.Mount(); // required before use...Mounting the dev Bucket before use is required. Mount is necessary to ensure the existence of tables and indexes.
A path is specified when a File is uploaded into a Bucket. Multiple uploads to the same path cause the file to be revisioned. Figure 3 below shows /video.mp4 uploaded and revisioned 5 times.
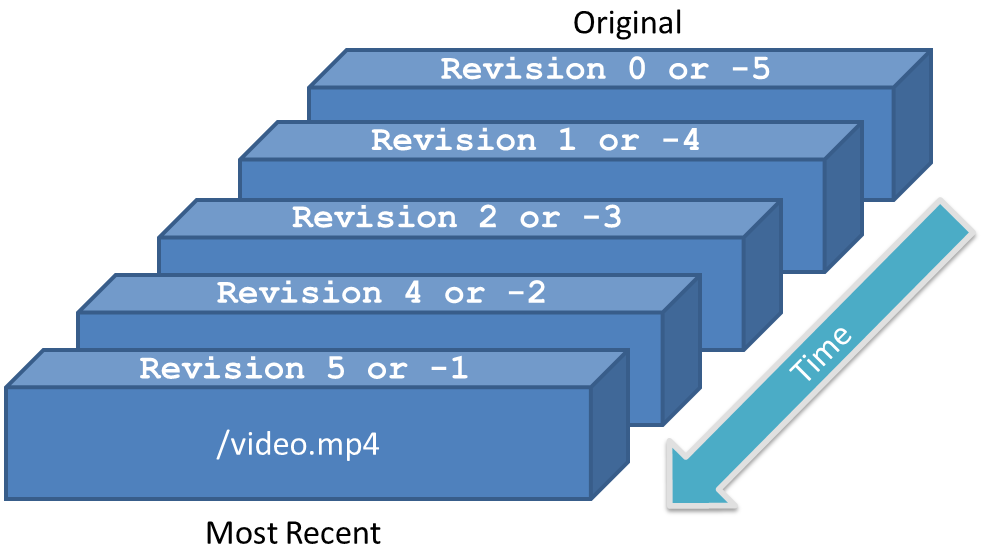
| Positive | Negative |
|---|---|
|
0: The original stored file. 1: The first revision. 2: The second revision. etc... |
- 1: The most recent revision. - 2: The second most recent revision. - 3: The third most recent revision. etc... |
The following code uploads a file to a Bucket:
// Upload a file using byte[]
var fileId = bucket.Upload("/video.mp4", videoBytes);
// Upload a file using an IO stream
Guid uploadId;
using( var fileStream = File.Open("C:\\video.mp4", FileMode.Open) )
using( var uploadStream = bucket.OpenUploadStream("/video.mp4") )
{
uploadId = uploadStream.FileInfo.Id;
fileStream.CopyTo(uploadStream);
}fileId will be the file reference for that specific revision. There are many methods on bucket that allow the use of IO streams and async methods.
UploadOptions can be specified to control the ChunkSizeBytes. This value controls the size of the document chunks stored in the RethinkDB. Optionally, additional variable Metadata can also be stored along with the uploaded file.
var opts = new UploadOptions();
opts.SetMetadata(new
{
UserId = "123",
LastAccess = R.Now(),
Roles = R.Array("admin", "office"),
ContentType = "application/pdf"
});
var id = bucket.Upload(testFile, TestBytes.HalfChunk, opts);
var fileInfo = bucket.GetFileInfo(id);
fileInfo.Metadata["UserId"].Value<string>().Should().Be("123");// Downloads to a byte[]
var bytes = bucket.DownloadAsBytesByName("/video.mp4");
// Download revision:0 to a file stream on the client
var localFileStream = File.Open("C:\\video_original.mp4", FileMode.Create);
bucket.DownloadToStreamByName("/video.mp4", localFileStream, revision: 0);
localFileStream.Close();Caution using DownloadAsBytes as it returns a byte[] with int.MaxValue as a maximum size. For relatively large files use DownloadToStream. DownloadToStream does not have any maximum size limit beyond the host's OS limitations on the client side.
ReGrid supports starting downloads at an offset by seeking into part of a large file.
var opts = new DownloadOptions {Seekable = true};
using( var stream = bucket.OpenDownloadStream("/video.mp4", options: opts) )
{
stream.Seek( 1024 * 1024 * 20, SeekOrigin.Begin);
//start reading 20MB into the file...
}By default, ReGrid will Soft delete files. Below shows a few examples of how to delete a file in ReGrid:
var file = bucket.GetFileInfoByName(testfile);
// Soft delete
bucket.DeleteRevision(file.Id, mode: DeleteMode.Soft);
// Hard delete
bucket.DeleteRevision(file.Id, mode: DeleteMode.Hard);Remember, multiple uploads to the same file path do not overwrite a file. Uploading files to the same path cause the file to be revisioned. Deleting a file is deleting a revision of that file.
A convenience method DeleteAllRevisions exists that deletes file revisions one-by-one, iteratively. If there is a failure during the iterative deletion, some revisions of the deleted files might still exist and may not appear fully removed from the file system.
Soft deletes simply set the status flag of a FileInfo document. This operation is fast and atomic.
Hard deletes, like Soft deletes, set the status flag of a FileInfo document. However, Hard delete operations involve deleting multiple documents. RethinkDB only supports atomic operations per document. So, a full and complete Hard delete on a logical File and its revision is inherently non-atomic at the physical layer. If the Hard delete operation fails and is incomplete, the GridUtility class contains operations to clean up and restart partially deleted files.
Recommended Usage: Always use Soft delete to delete files. Space can be reclaimed later by using the GridUtility class to reclaim space occupied by Soft deleted files and associated chunks. If overwrite semantics are desired, delete the original file before uploading a new file to the same path.
- Home
- Query Examples
- Logging
- Connections & Pooling
- Extra C# Features
- GOTCHA Goblins!
- LINQ to ReQL Provider
- Differences
- Java ReQL API Documentation