This project's objective is to train a Natural Language Processing model using quantum methods, using the libarary lambeq
- Python 3.8+
- Pipenv
- Basic natural language processing
- Basic quantum computing knowledge
This project uses a the dataset named sentiment140, which is filled with around 1,6 million of tweets, using the following classification:
- 0 = negative
- 2 = neutral
- 4 = positive
Since the tweets
This dataset can be downloaded from here
A quantum circuit is a computational routine consisting of coherent quantum operations on quantum data, such as qubits, and concurrent real-time classical computation. It is an ordered sequence of quantum gates, measurements and resets, all of which may be conditioned on and use data from the real-time classical computation.
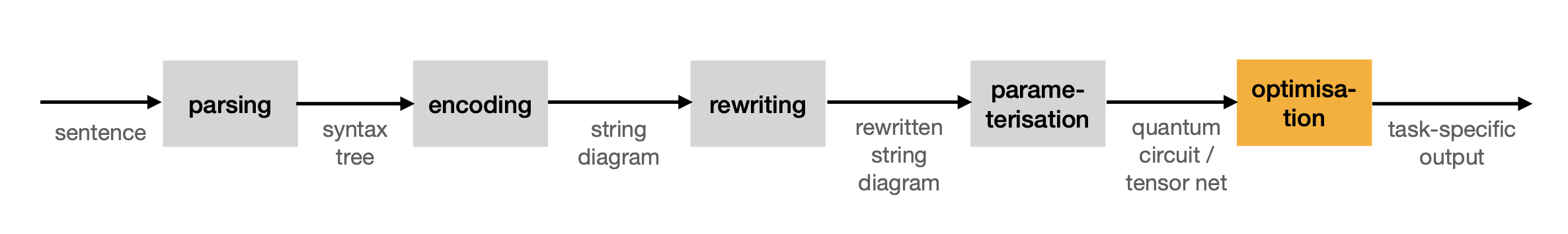
The library lambeq uses the pipeline shown in the image below to convert a sentence to a quantum circuit. The output of this pipeline can be a quantum circuit or a tensor network, both of this objects can be used for traning.
Before inputing the data into the pipeline, it is important to do a cleaning phase. In this stage, hashtags and usernames written in the tweets are deleted because this information can become noise for the training, testing and validation phases.
The first part of the process in lambeq given a sentence, is to convert it into a string diagram, according to a given compositional scheme. lambeq can accommodate any compositional model that can encode sentences as string diagrams, its native data structure.
Syntactic derivations in pregroup form can become extremely complicated, which may lead to excessive use of hardware resources and prohibitively long training times. The purpose of the rewrite module is to provide a means to the user to address some of these problems, via rewriting rules that simplify the string diagram.
Up to this point of the pipeline, a sentence is still represented as a string diagram, independent of any low-level decisions such as tensor dimensions or specific quantum gate choices. This abstract form can be turned into a concrete quantum circuit or tensor network by applying ansätze. An ansatz can be seen as a map that determines choices such as the number of qubits that every wire of the string diagram is associated with and the concrete parameterised quantum states that correspond to each word.
There are many ways to train a lambeq model, and the right one to use depends on the task at hand, the type of experiment (quantum or classical), and even other factors, such as hardware requirements. In this case we are using a classical experiment with pytorch, for this case, the steps to train are:
- Extract the word symbols from all diagrams in a set to create a vocabulary.
- Assign tensors to each one of the words in the vocabulary.
- Training loop:
- For each diagram, associate tensors from the vocabulary with words.
- Contract the diagram to get a result.
- Use the result to compute loss.
- Use loss to compute gradient and update tensors.