本项目所涉及到的技术栈:React、TypeScript 、StoryBook、sass
第三方库的使用:react-transtion fontawesome、axios、classnames
React 是组件的世界,创造各种组件就是它的终极目标。
所以我打算仿照 Antd 的源码准备自己先写一些基础的组件(之前实习的时候也对 antd 的基础组件进行了二次封装,所以有一点经验),同时也为了夯实基础知识、也算是对自己的一种考验吧~
这里记录一下遇到的问题以及解决方法
定制一系列主题变量、然后应用到各个组件上
$white: #fff !default;
$gray-100: #f8f9fa !default;
$gray-200: #e9ecef !default;
$gray-300: #dee2e6 !default;
$gray-400: #ced4da !default;
$gray-500: #adb5bd !default;
$gray-600: #6c757d !default;
$gray-700: #495057 !default;
$gray-800: #343a40 !default;
$gray-900: #212529 !default;
···Mixin 的使用,是可以重用的代码块。
使用@mixin 命令,定义一个代码块。
@mixin left {
float: left;
include margin-left: 10px;
}使用@include 命令,调用这个 mixin
div {
@include left;
}mixin 的强大之处,在于可以指定参数和缺省值。
@mixin left($value: 10px) {
float: left;
margin-right: $value;
}
使用的时候,根据需要加入参数:
div {
@include left(20px);
}
统一导出
@import "./variables";
// layout
@import "./reboot";
// mixin
@import "./mixin";
// animation
@import "../styles/animation";
// Button
@import "../components/Button/style" ···;(一)、Button
开发流程:
1、确定类型
2、定义接口
3、从 props 取出参数
4、根据属性计算classes
5、根据参数UI组件
6、编写测试 case
7、最后编写 stories 方便预览
首先需要了解 react 官方定义的 ts 类型 例如 ReactNode, FC, ButtonHTMLAttributes,AnchorHTMLAttributes
使用 ts 时、我们需要考虑到各个参数的类型、确定类型,定义接口,使用接口去规范和约束代码
这里遇到一个问题:ts 高级类型
(1)button 上的属性有可能在 button 上的必须的 但是在 a 上不能填写 button 必须的属性 反之亦然 所以需要把属性设置为可选的 Partial
Partial的作用就是将某个类型里的属性全部变为可选项?。
// React.ButtonHTMLAttributes<HTMLButtonElement> 拿到button所有原生属性
// NativeButtonProps 为原生属性和扩展属性的集合
type NativeButtonProps = BaseButtonProps & ButtonHTMLAttributes<HTMLElement>;
type AnchorButtonProps = BaseButtonProps & AnchorHTMLAttributes<HTMLElement>;
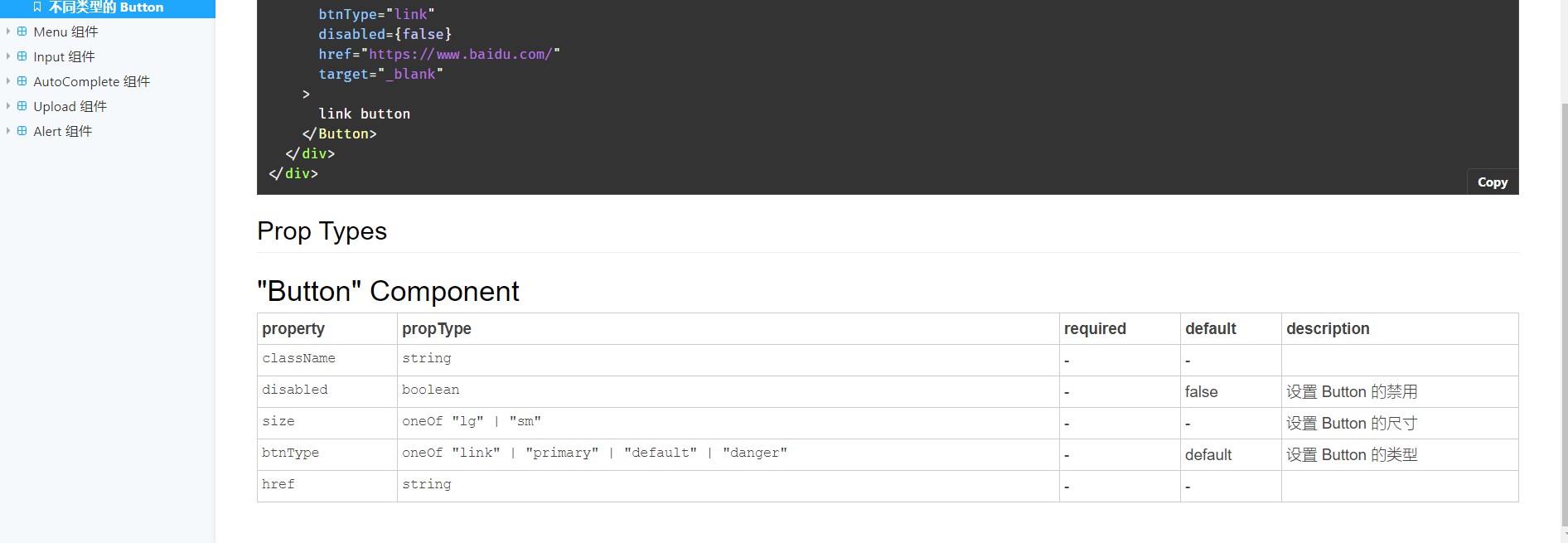
export type ButtonProps = Partial<NativeButtonProps & AnchorButtonProps>;主要代码~ 可以看出 button 组件还是非常简单的
const classes = classNames("btn", className, {
[`btn-${size}`]: size,
[`btn-${btnType}`]: btnType,
disabled: btnType === "link" && disabled,
});
if (btnType === "link") {
return (
<a href={href} className={classes} {...restProps}>
{children}
</a>
);
} else {
return (
<button disabled={disabled} className={classes} {...restProps}>
{children}
</button>
);
}测试 case 这里使用的是jest react 默认支持的测试框架 很好用 使用它需要看看文档、学习基础测试如何编写
简单示例
const sum = require("./sum");
test("adds 1 + 2 to equal 3", () => {
expect(sum(1, 2)).toBe(3);
});button 测试 case 刚开始眼睛看晕了~~~
describe('test Button component', () => {
it('should render the correct default button', () => {
const wrapper = render(<Button {...defaultProps}>nice</Button>)
const element = wrapper.getByText('nice') as HTMLButtonElement
expect(element).toBeInTheDocument()// 证明元素存在
expect(element.tagName).toEqual('BUTTON')
expect(element).toHaveClass('btn btn-default')
expect(element.disabled).toBeFalsy()
fireEvent.click(element)
expect(defaultProps.onClick).toHaveBeenCalled()
})
it('should render the correct component based on different props', () => {
const wrapper = render(<Button {...testProps}>nice</Button>)
const element = wrapper.getByText('nice')
expect(element).toBeInTheDocument()
expect(element).toHaveClass('btn-primary btn-lg klass')
})
it('should render a link when btnType equals link and href is provided', () => {
const wrapper = render(<Button {...testProps} btnType='link' href='https://www.baidu.com/'>nice</Button>)
const element = wrapper.getByText('nice')
expect(element).toBeInTheDocument()
expect(element.tagName).toEqual('A')
expect(element).toHaveClass('btn btn-link')
})
it('should render disabled button when disable set to true', () => {
const wrapper = render(<Button {...disabledProps}>nice</Button>)
const element = wrapper.getByText('nice') as HTMLButtonElement
expect(element).toBeInTheDocument()
expect(element.disabled).toBeTruthy()
fireEvent.click(element)
expect(disabledProps.onClick).not.toHaveBeenCalled()
})
})最后一步 编写 stories 文件 展示我们的 button
const defaultButton = () => (
<Button onClick={action("clicked")}>default button</Button>
);
const buttonWithSize = () => (
<div>
<Button size="lg">large button</Button>
<Button size="sm">small button</Button>
</div>
);
const buttonWithType = () => (
<div>
<Button btnType="danger">danger button</Button>
<Button btnType="primary">primary button</Button>
<Button btnType="link" target="_blank" href="https://www.baidu.com/">
link button
</Button>
</div>
);
storiesOf("Button 组件", module)
.add("Button", defaultButton)
// .add('不同尺寸的 Button', buttonWithSize, {info: {inline: false}})
.add("不同尺寸的 Button", buttonWithSize)
.add("不同类型的 Button", buttonWithType);效果
到这组件就算完成了~~~
(二)Menu 组件
横向模式纵向模式处理的方式会有不同
由于 props.children 可以说任意类型的、如果 children 是函数,那么调用 map 就会报错~但是我们只希望 children 是 Menu.SubMenu 于是
SubMenu.displayName = 'SubMenu'
·······························
const { displayName } = childElement.type
if (displayName === 'MenuItem') {
return React.cloneElement(childElement, {
index: `${index}-${i}`
})
} else {
console.error(
'warning: Menu has a child which is not a MenuItem component'
)
}react 内置属性帮助我们判断类型,cloneElement 该方法以 element 作为起点,克隆并返回一个新的 React 元素。所产生的元素将具有原始元素的 props ,新的 props 为浅层合并。 新的子元素将取代现有的子元素, key 和 ref 将被保留,之所以使用这个方法是因为我们需要知道是那个 menu 被选中了,另外就是过渡动画的实现依靠 react-transtion这个库了,对一些动画细节的处理、多看文档 unMountOnExit(默认情况下,子组件在达到“退出”状态后仍然挂载。如果你希望在组件退出后卸载组件,就要设置unmountOnExit)、为什么要这样:因为使用添加切换类名的方式的时候如果设置了 display:none 那么所有的动画将会失效,所以需要封装一个动画过渡组件~~~
(三)Input 组件
ts Omit 方法的使用
// Omit用来忽略InputHTMLAttributes里的size 这样就不会产生冲突
export interface InputProps
extends Omit<InputHTMLAttributes<HTMLElement>, "size"> {
/**设置 Input 的禁用 */
disabled?: boolean;
/**设置 Input 的尺寸 */
size?: InputSize;
/**设置 Input 的图标 */
icon?: IconProp;
/**在 Input 之前放置元素 */
prepend?: string | ReactElement;
/**在 Input 之后放置元素 */
append?: string | ReactElement;
onChange?: (e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => void;
}这里实现了一个受控组件,类似于 vue 中 v-model
const ControlledInput = () => {
const [value, setValue] = useState("");
return (
<Input
value={value}
defaultValue={value}
onChange={(e) => {
setValue(e.target.value);
}}
/>
);
};还有一些细节处理~~~
(三)Icon组件
组件就基本上完全依靠第三方库来实现了、算是掌握了fortawesome的使用吧~~~
(四) AutoComplete 组件
Input输入内容自动联想
做了loading等待状态,异步发送请求,自定义渲染子列表,支持 Input 组件的所有属性 支持键盘事件选择
自定义Hook实现防抖效果
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function useDebounce(value: any, delay = 300) {
const [debouncedValue, setDebouncedValue] = useState(value);
useEffect(() => {
const handler = setTimeout(() => {
setDebouncedValue(value);
}, delay);
return () => {
clearTimeout(handler);
};
}, [value, delay]);
return debouncedValue;
}
export default useDebounce;
// useEffect 处理函数的副作用 当useEffect函数返回一个函数的时候代表着下次update的时候清理函数的副作用
// 这里正好利用这一点来clear选中状态是怎么实现的~ 会传一个index和当前的index比较,如果相同那么就是选中状态
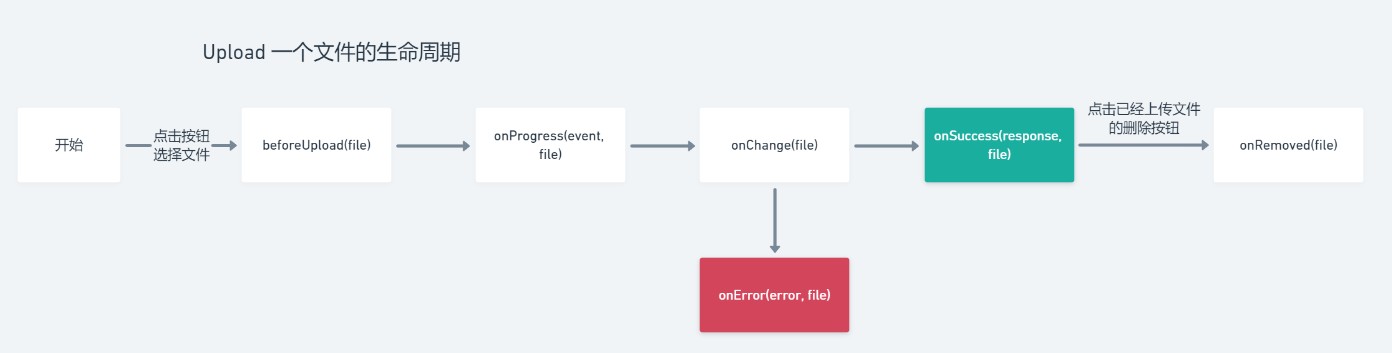
(五)Upload组件
这个相对比较复杂、做了上传进度条显示、上传状态展示、以及上传结果展示
1、事件代理
const handleClick = () => {
if (uploadRef.current) {
uploadRef.current.click();
}
};2、多个文件上传 遇到的bug
setFileList([_file, ...fileList]); bug 多个文件上传的时候 只有一个文件显示 异步更新的bug 需要回调函数来解决
setFileList((prevFile)=>{
return ....
})3、声明周期
(1)上传前的生命周期实现
const uploadFiles = (files: FileList) => {
const postFile = Array.from(files);
postFile.forEach((file) => {
if (!beforeUpload) {
post(file);
} else {
const result = beforeUpload(file);
if (result && result instanceof Promise) {
result.then((progressFile) => {
post(progressFile);
});
} else if (result !== false) {
post(file);
}
}
});
};(2)上传中需要显示进度条
axios
.post(action, formData, {
headers: {
...headers,
"Content-Type": "multiple/form-data",
},
// 支持携带cookie 这是axios默认支持的功能
withCredentials,
onUploadProgress: (e) => {
let percentage = Math.round((e.loaded * 100) / e.total) || 0;
if (percentage < 100) {
updataFileList(_file, { percent: percentage, status: "uploading" });
if (onProgress) {
onProgress(percentage, _file);
}
}
},
})
.then((resp) => {}axios本身支持
(3)拖动上传的实现
export const Dragger: FC<DraggerProps> = (props) => {
const { onFile, children } = props;
const [dragOver, setdragOver] = useState(false);
const classes = classNames("uploader-dragger", {
"is-dragover": dragOver,
});
const handleDrag = (e: DragEvent<HTMLElement>, over: boolean) => {
e.preventDefault();
setdragOver(over);
};
const handleDrop = (e: DragEvent<HTMLElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
setdragOver(false);
onFile(e.dataTransfer.files);
};
return (
<div
className={classes}
onDragOver={(e) => {
handleDrag(e, true);
}}
onDragLeave={(e) => {
handleDrag(e, false);
}}
onDrop={handleDrop}
>
{children}
</div>
);
};主要是drag事件的 使用其他的逻辑问题与点击上传相同
3、测试使用以及发布npm
npm link 软连接到本地测试项目进行测试没有异常后 可以进行发布
注册账号
npm whoami 检查是否登陆
npm adduser 创建账号
npm login 登陆账号
// 发布前执行
package.json
"scripts": {
// "prepublish": "npm run build-lib" // 即将废弃
"prepublishOnly": "npm run build-lib" // 发布前要做的事
}
"files": [ // 表示要把哪些资源上传到npm仓库上去,不写默认使用 .gitignore 内的信息
"lib"
],
npm publish 发布包打包需要注意的事情
解决用户安装我们的包时安装了两份react和react-dom库
用户在安装时,该处声明的依赖不会被安装
"peerDependencies": {
"react": ">=16.8.0",
"react-dom": ">=16.8.0"
},
删除 dependencies 内的两个依赖
"react": "^16.13.1",
"react-dom": "^16.13.1",
然而开发时还要使用,所以将删除的引用,重新添加到devDependencies中
"devDependencies": {
"react": "^16.13.1",
"react-dom": "^16.13.1",
}