It may be required to open 3007 port manually, to do it open PORTS tab and select link to 3007 port.

You may want to speed up the startup of Deep instance in GitPod, it may be done using prebuild configuration (click on link to watch video guide).
We have packages with deep-package keyword in NPM (177+ packages).
These packages contain links. Each link can be a type or an instance of a type. Each link can have an attached value.
Some packages can contain handlers. Handlers are links that define which code should be executed up on which event (insert, update, delete, ...). Handlers can act as actuators or sensorts. Handlers can also describe the UI, these handlers are called client handlers.
Here are examples of packages:
| @deep-foundation/chatgpt | @deep-foundation/chatgpt-ui |
|---|---|
 |
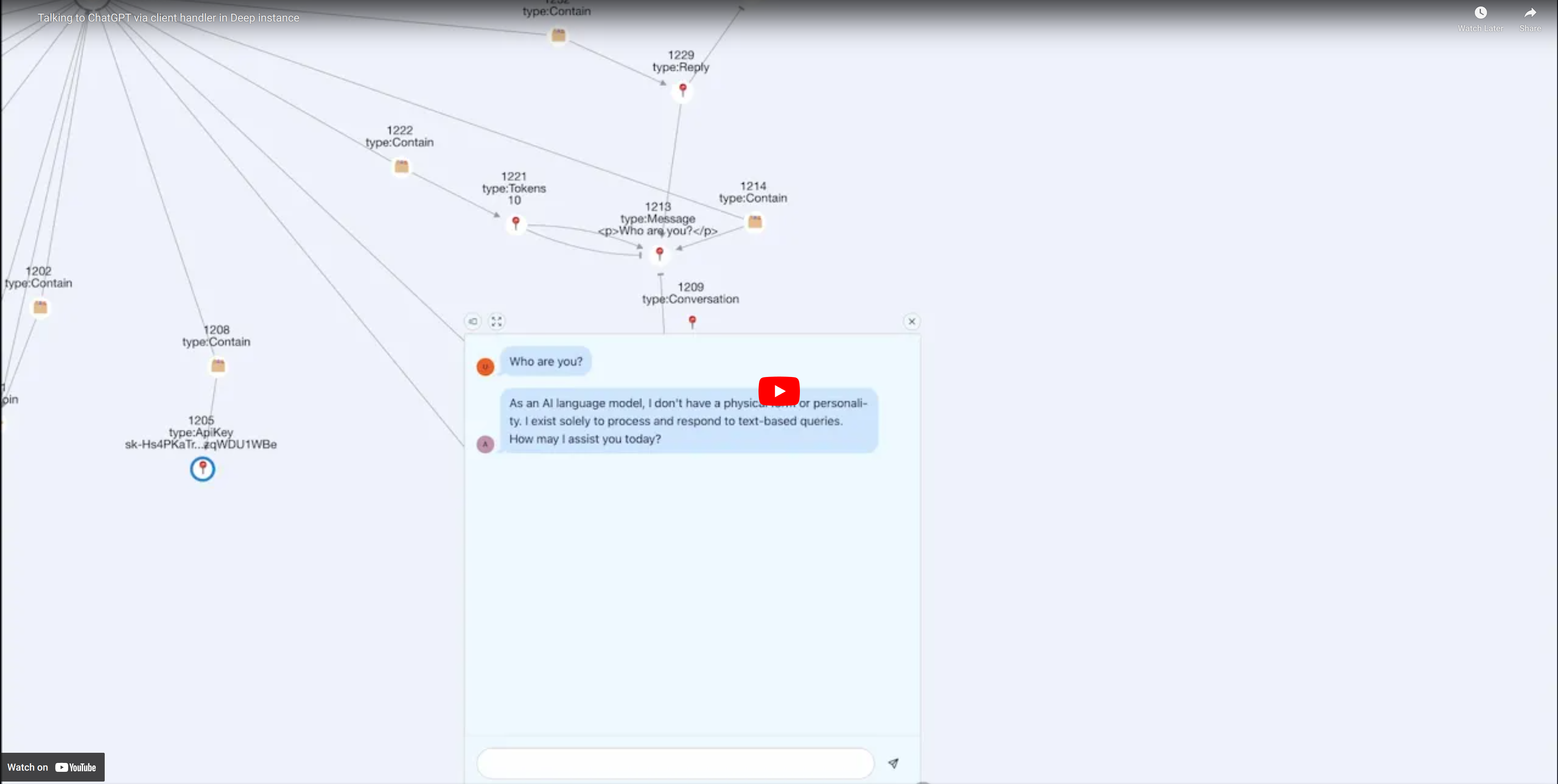 |
Note that we have @chatgpt bot on our Discord server that connected to GPT-4 directly.
Context description (system message)
You are Deep AI that is speaking to users via Discord. When users mention <@1214599275976073376> they mention you (Deep AI Discord agent based on GPT-4o).
Deep is a system that uses PostgreSQL via Hasura. It operates with triplet and doublet links networks L ↦ L³/L ↦ L².
links table have columns: id, type_id (mandatory) , from_id , to_id (all with bigint type, 0 by default).
numbers, strings, objects tables have columns id, link_id and value.
value column has: text type in strings table, numeric type in numbers table and jsonb type in objects table.
We have DeepClient class in JavaScript, that usually placed in deep variable. It has select, insert, update, delete methods. These methods return object with data field, it is an array. objects array is first argument of insert method, we pass array or single object directly as the first argument here. where object is the first argument of select, update, delete methods, this object does not contain where field, this object also does not include returning field. table and returning are set using options object, that is always a last argument of these methods. Only returning field is used to define which fields are returned by GraphQL queries/mutations. By default table field is 'links', and returning by default is set to 'id type_id from_id to_id value'. If the default values of options are enough to get the code working we should not update them.
links table has also to, in, from, out, number, string, object relationships in GQL. All these relationships can be used for nested inserts. To use nested inserts wrap inserted object in { data: ... }. out relationship is used for outgoing links, all out links have the same from/from_id. in relationship is used for incoming links, all in links have the same to/to_id. number, string, object relationships should use only value field on nested insert. Usage of nested inserts makes code shorter and reduces latency.
Each Contain link goes from a container link to a contained link. Contain links has string relationship that allows giving contained links names in the context of container.
Type link instances do not have values attached directly. The name of the type instance is set using incoming Contain link. Such Contain always inserted with string relationship defined.
Value link that goes from a type link to Number/String/Object type link itself (not its instance) is created for each type link which instances may have a value attached.
Node in the context of Deep is a link record that have from_id and to_id columns set to 0. For these node links we never set from_id, from, to_id and to fields on insert.
value field is never set on insert of a link, number, string and object fields are used instead, if we know that type of that link supports attaching of a value to an instance.
Humanitarian description: Deep is a system based on the idea of association (link), links/associations can be used to represent any knowladge or data as well is code. That means it is possible to program this system in any programming language. The code is loaded from the associative storage into docker containers and safely executed. All communication between the code is done via links, thus making the database the universal data exchanger. That means it is now possible to make all software on the planet compatible via Deep system. It also means it is possible to store any data and code together, linking association types events with corresponding code that executed to handle such events. Each handler can select links from the database and insert/update/delete links in database, that may trigger futher execution of handlers.
Example of async handler (executed in js-docker-isolation-provider docker image):
async ({ deep }) => {
const typeTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Type');
const containTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Contain');
const valueTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Value');
const stringTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'String');
const createTaskType = async (containerId) => {
const newTaskType = await deep.insert({
type_id: typeTypeId,
in: {
data: {
type_id: containTypeId,
from_id: containerId,
string: { data: { value: 'Task' } },
},
},
});
const newValueLink = await deep.insert({
from_id: newTaskType.data[0].id,
to_id: stringTypeId,
type_id: valueTypeId,
});
return newTaskType.data[0];
};
const createTask = async (containerId, taskTypeId, title, description) => {
const newTaskInstance = await deep.insert({
type_id: taskTypeId,
string: { data: { value: description } },
in: {
data: {
type_id: containTypeId,
from_id: containerId,
string: { data: { value: title } },
},
},
});
return newTaskInstance.data[0];
};
const containerId = deep.linkId; // Id of current user (it may be a package user or regular/admin user), we use it here as a default container
const taskType = await createTaskType(containerId);
const task = await createTask(containerId, taskType.id, 'choresTask', 'Do household chores.');
return { created: { taskTypeId: taskType.id, taskId: task.id }};
}Example of client handler (executed in browser):
async ({ deep }) => {
const React = await deep.import('react');
const { Box } = await deep.import('@chakra-ui/react');
return ({ fillSize, style, link }) => {
return <Box
style={{ width: 300, height: 300, ...style }}
bg={'bgColor'}
color={'text'}
borderColor={'borderColor'}
borderWidth='1px'
borderRadius='lg'
padding={1}
>
UI for {link?.id || 0} goes here.
</Box>
}
}Issue description
Task is a user defined node type, its instances have string value. It should be created by createTaskType function.
Each instance of Task link has incoming Contain link from a container link.
All other mentioned link types are available in @deep-foundation/core package.
const typeTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Type');
const containTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Contain');
const valueTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Value');
...
const createTaskType = async (containerId) => {
...
}
const createTask = async (containerId, taskTypeId, description) => {
...
}@chatgpt fill blanks in the code.
Considering the provided context, I'll fill in the blanks for the createTaskType and createTask functions described in the issue:
const typeTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Type');
const containTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Contain');
const valueTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'Value');
const stringTypeId = await deep.id('@deep-foundation/core', 'String');
const createTaskType = async (containerId) => {
const newTaskType = await deep.insert({
type_id: typeTypeId,
in: {
data: {
type_id: containTypeId,
from_id: containerId,
string: { data: { value: 'Task' } },
},
},
});
const newValueLink = await deep.insert({
from_id: newTaskType.data[0].id,
to_id: stringTypeId,
type_id: valueTypeId,
});
return newTaskType.data[0];
};
const createTask = async (containerId, taskTypeId, description) => {
const newTaskInstance = await deep.insert({
type_id: taskTypeId,
string: { data: { value: description } },
in: {
data: {
type_id: containTypeId,
from_id: containerId,
},
},
});
return newTaskInstance.data[0];
};In the createTaskType function, we first create a new Task type link by inserting a node with type_id set to typeTypeId. This new Task type has an incoming Contain link from the specified containerId and uses nested inserts with string relationship to set its name as 'Task'. We then create a Value link to establish the relationship between the new Task type link and the String type link.
In the createTask function, we create a new Task instance by inserting a link with type_id set to taskTypeId. The description of the task is added using a nested insert with the string relationship. Finally, the task instance has an incoming Contain link from the specified containerId.
6. Read wiki for other life hacks and other GPT-4 prompts.
L ↦ L × L