-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
149 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,149 @@ | ||
| --- | ||
| title: "Introduction to UML" | ||
| layout: notes | ||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| # UML | ||
| * *Unified Modeling Language* | ||
| * Standardized, general-purpose modeling language | ||
| * Purpose: visualize, specify, construct, and document artifacts of software systems | ||
| * Consolidation OO development methods and notations of: | ||
| - Booch Method [Booch] | ||
| - Object-Modeling Technique (OMT) [Rumbaugh, et. al.] | ||
| - Object-Oriented Software Engineering (OOSE) [Jacobsen] | ||
|
|
||
| * Object-Management Group [www.omg.org](http://www.omg.org/) | ||
|
|
||
| # Modeling History | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # Diagram Types | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
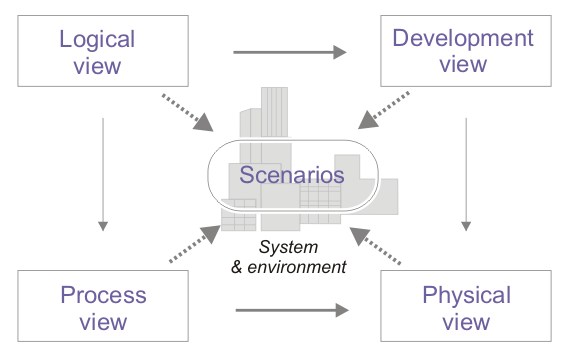
| # Diagram Views Diagram | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # Diagram Views | ||
| * Logical view - concerned with the functionality the system provides end-users, includes Class and State diagrams. | ||
| * Process view - deals with the dynamic aspects of the system. E.g., it captures the concurrency and synchronization aspects of the design, includes Sequence and Activity diagrams. | ||
| * Development view - describes the static organization of the software in its development environment (a programer's perspective view), includes Component and Package diagrams | ||
|
|
||
| # Diagram Views (continued) | ||
| * Physical view - describes the mapping(s) of the software onto the hardware and reflects its distributed aspect, includes Deployment diagram | ||
| * Scenarios - description of architecture illustrated using a small set of use cases (or scenarios), includes Use Cases and Use Case Diagram | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # Structure Diagrams - Static Aspects | ||
| * *Class* | ||
| * *Object* | ||
| * *Component* | ||
| * *Deployment* | ||
| * *Package* | ||
|
|
||
| # Class Diagrams | ||
| * Set of classes and their relationships. Describes interface to the class | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # Object Diagrams | ||
| * Set of objects (class instances) and their relationships | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
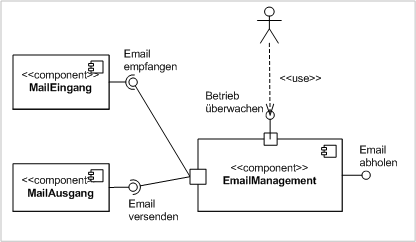
| # Component Diagrams | ||
| * Logical groupings of elements and their relationships | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
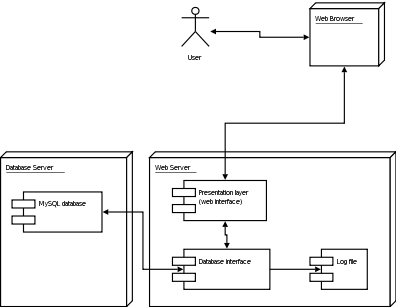
| # Deployment Diagrams | ||
| * Set of computational resources (nodes) that host each component | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
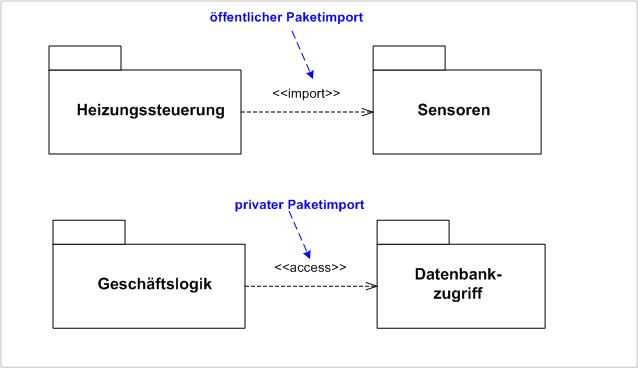
| # Package Diagram | ||
| * Organization into packages | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # Behavior Diagrams - Dynamic Aspects | ||
| * *Use Case* | ||
| * *Sequence* | ||
| * *Communication* | ||
| * *State Chart* | ||
| * *Activity* | ||
|
|
||
| # Use Case Diagram | ||
| * High-level behaviors of the system, user goals, external entities: actors | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # Sequence Diagram | ||
| * Time ordering of messages | ||
|
|
||
| 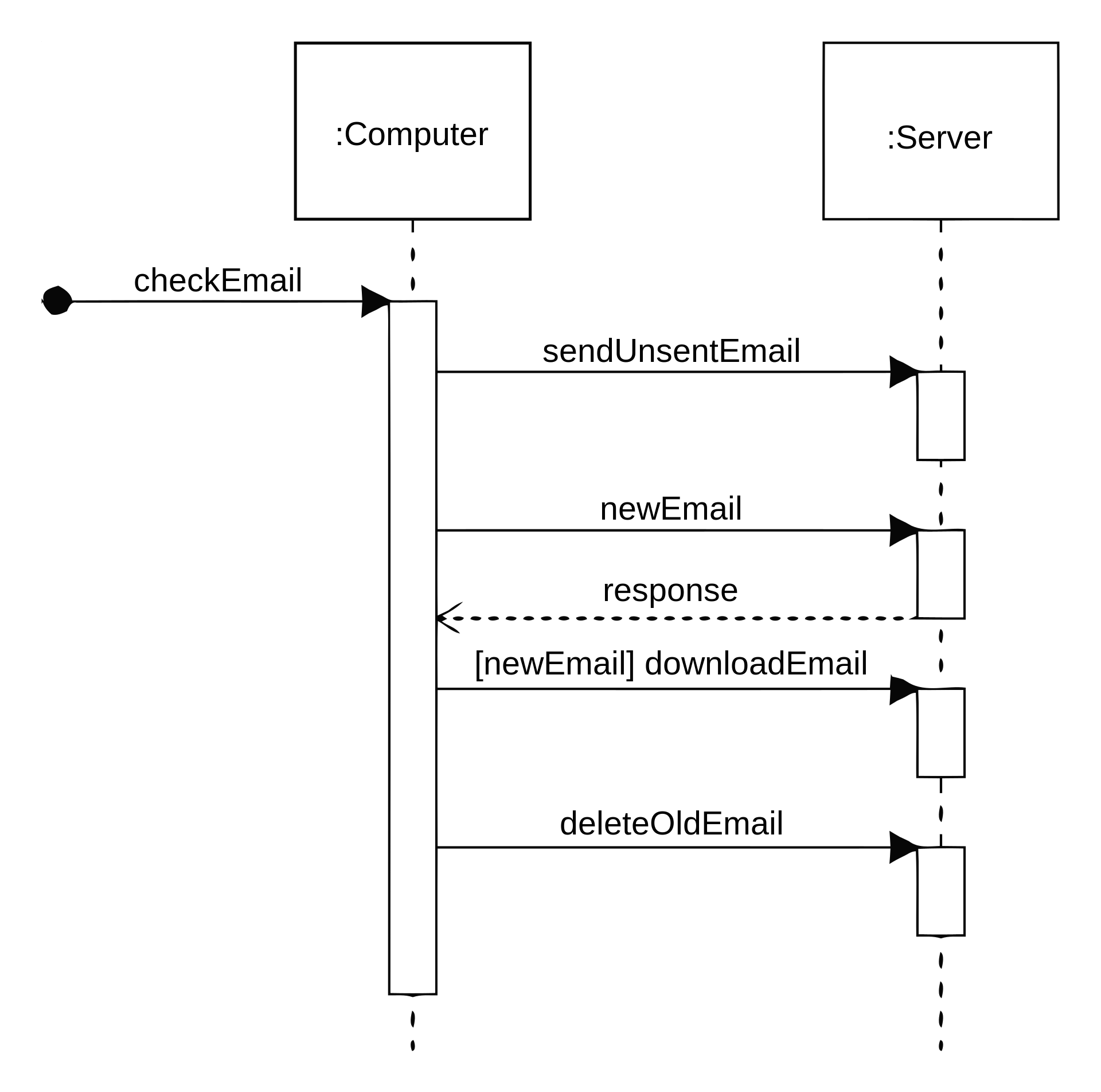 | ||
|
|
||
| # Communication Diagram | ||
| * Structural organization of objects and messages | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # State Machine Diagram | ||
| * Event driven state changes of system | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # Activity Diagram | ||
| * Flow of control between activities | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # [UmlMode](http://martinfowler.com/bliki/UmlMode.html) [[Fowler](http://martinfowler.com/)] | ||
| * [UmlAsProgrammingLanguage](http://martinfowler.com/bliki/UmlAsProgrammingLanguage.html) | ||
|
|
||
| * [UmlAsBlueprint](http://martinfowler.com/bliki/UmlAsBlueprint.html) | ||
| * [UmlAsSketch](http://martinfowler.com/bliki/UmlAsSketch.html) | ||
|
|
||
| # [UmlAsProgrammingLanguage](http://martinfowler.com/bliki/UmlAsProgrammingLanguage.html) | ||
| * Provide enough detail to compile executable code from UML | ||
| * Promise | ||
| * UML is a higher-level language and thus more productive than current programming languages | ||
| * Reality: | ||
| * Graphical languages are not always better, e.g., flow chart versus pseudocode for an algorithm | ||
|
|
||
| # [UmlAsBlueprint](http://martinfowler.com/bliki/UmlAsBlueprint.html) | ||
| * Express design enough to hand off to other group | ||
| * Separation of labor: High-end designers versus "coders" | ||
| * Main feature: Completeness. | ||
| * Forward engineering - Every detail needed to implement the design | ||
| * Reverse engineering - Every detail of what design is in the code | ||
| * Specialized tools to generate and create | ||
| * May be integrated into IDE and used as another view of the code | ||
|
|
||
| # [UmlAsSketch](http://martinfowler.com/bliki/UmlAsSketch.html) | ||
| * UML to communicate an aspect of a system | ||
| * Forward engineering - sketches to work out design before implementation | ||
| * Reverse engineering - sketches for comprehension | ||
| * Main feature: Selectivity. | ||
| * Requirements: Need to be performed quickly and collaboratively | ||
| * E.g., whiteboard, papers | ||
|
|
||
| # UML & Process | ||
| * UML is not a process | ||
| * UML supports a process | ||
| * Not all diagrams in UML are useful to all processes and all development | ||
| * How UML is used in a process is affected by the UmlMode | ||
|
|
||
| # UML-Driven Process | ||
| * *Requirements*: Written text, Use Case Diagrams | ||
| * *Analysis* Object Diagrams | ||
| * *High-level Design* Class Diagram | ||
| * *Low-level Design* Sequence Diagram, State Machine Diagram (perhaps) | ||
| * *Implementation* Deployment Diagram, Activity Diagram | ||
|
|
||
| # Problems with UML | ||
| * Limited to no formal semantics | ||
| * Diagram representation: layout versus model |