PhySpeTree is implemented in Python language (supports Python2.7+ and Python3+), designed for Linux systems (docker for Windows OS or Mac OS).
Documents: PhySpeTree documentation.
Understanding phylogenetic relationships between different species is crucial for evolutionary studies. Reconstructing the phylogenetic species tree, a branching diagram, is particularly useful in inferring evolutionary relationships. For example, the tree-of-life provides a remarkable view of organizing principles of the biological world. So, the exact species tree to be reconstructed is necessary, but the process of reconstructing the species or gene tree is very tedious.
Here, we developed an easy-to-use package named PhySpeTree that is convenient to reconstruct species trees by one command line. Two independent pipelines were included by using the most adopted small subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU rRNA) and concatenated highly conserved proteins (HCP), respectively. A distinct advantage is that users only need to input species names and PhySpeTree automatically downloads and analyzes sequences of SSU rRNA or HCP from about 4,000 organisms.
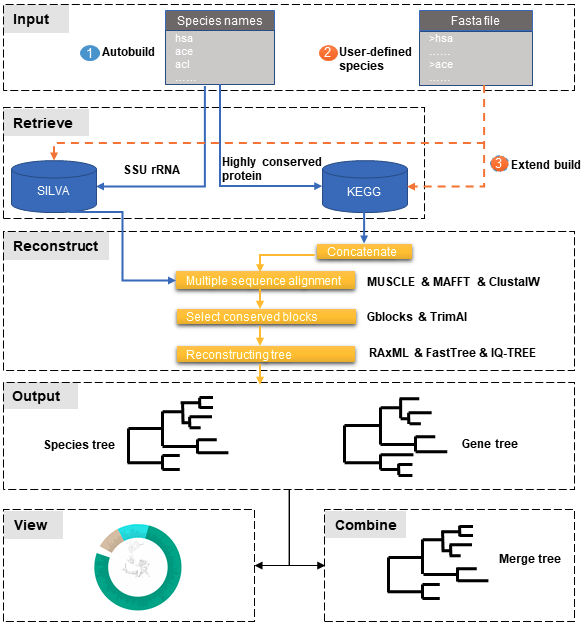
PhySpeTree workflow includes the following steps:
- ① Automatic tree reconstruction.
- ② Processing user-defined fasta files for unannotated organisms.
- ③ Reconstructing species trees with unannotated organisms.
- Inputs only include species names.
- One command line to build trees.
- HCP and SSU rRNA methods.
- Combine trees.
- View trees with iTOL.
- Versatile software with adjustable parameters.
- PyPI
$ pip install PhySpeTreeor download PhySpeTree and install:
$ pip install PhySpeTree-*.tar.gzTo upgrade to latest version:
$ pip install --upgrade PhySpeTree- GitHub
$ git clone [email protected]:yangfangs/physpetools.git
$ cd physpetools
$ python setup.py installor download and install:
$ pip install physpetools-*.tar.gzThe input of autobuild module is a TXT file containing abbreviated species names, for example organism example list.
Use autobuild in command line like this:
$ PhySpeTree -i organism_example_list.txt [options]*| -h | Print help message and exits. |
| -i | Input a TXT file containing abbreviated species names. |
| -o | A directory to store outputs. The default is "Outdata". |
| -t | Number of processing threads (CPUs). The default is 1. |
| -e | FASTA format files to extend the tree with the --ehcp or --esrna option. |
| --hcp | HCP (highly conserved protein) method (default). |
| --ehcp | HCP method with extended HCP sequences. |
| --srna | SSU method. |
| --esrna | SSU rRNA method with extended SSU rRNA sequences. |
Advanced options of internal software called in PhySpeTree can be set. These options are enclosed in single quotes and start with a space.
Here is an example of setting RAxML advanced options by --raxml_p:
$ PhySpeTree autobuild -i organism_example_list.txt -o test --srna --raxml --raxml_p ' -f a -m GTRGAMMA -p 12345 -x 12345 -# 100 -n T1'| --muscle | Multiple sequence alignment by MUSCLE (default). | ||||||||||
| --muscle_p | Set Muscle advance parameters. The default is
| ||||||||||
| --clustalw | Multiple sequence alignment by clustalw2. | ||||||||||
| --clustalw_p | Set clustalw2 advance parameters. Here use clustalw default parameters, please see Clustalw Help. | ||||||||||
| --mafft | Multiple sequence alignment by mafft. | ||||||||||
| --mafft_p | Set mafft advance parameters. Here use mafft default parameters, please see mafft algorithms. | ||||||||||
| --gblocks | Trim by Gblocks.(default) | ||||||||||
| --gblocks_p | Set Gblocks advance parameters, please see Gblocks documentation.
| ||||||||||
| --trimal | Trim by trimal. | ||||||||||
| --trimal_p | Set trimal advance parameters, please see trimal command line. | ||||||||||
| --raxml | Reconstruct phylogenetic tree by RAxML (default). | ||||||||||
| --raxml_p | Set RAxML advanced parameters. The default is
| ||||||||||
| --fasttree | Reconstruct phylogenetic tree by FastTree. | ||||||||||
| --fasttree_p | Set FastTree advance parameters, please see FastTree. | ||||||||||
| --iqtree | Reconstruct phylogenetic tree by iqtree. | ||||||||||
| --iqtree_p | Set iqtree advance parameters, please see IQ-TREE. |
The build module is used to reconstruct species trees with manually prepared sequences. Advanced options are the same as autobuild module.
Use build in command line to reconstruct phylogenetic tree:
- build phylogenetic tree by multiple method:
$ PhySpeTree build -i example_hcp -o output --multiple- build phylogenetic tree by SSU rRNA method:
$ PhySpeTree build -i example_16s_ssurna.fasta -o output --single| -h | Print help message and exits. |
| -i | Input a TXT file containing abbreviated species names. |
| -o | A directory to store outputs. The default is "Outdata". |
| -t | Number of processing threads (CPUs). The default is 1. |
| --multiple | Specify concatenate highly conserved protein method to reconstruct phylogenetic tree. The default method. |
| --single | Use SSU rRNA data to reconstruct phylogenetic tree. |
The combine module is used to combine trees generated from different methods. It contains two steps, at first merge different tree files into the same file. You can use cat bash command in the Linux system, for example:
$ cat tree1.tree tree2.tree > combineTree.treeThen, use combine
$ PhySpeTree PhySpeTree combine -i combineTree.tree [options]*| -h | Print help message and exits. |
| -i | Input PHYLIP format file containing multiple trees. |
| -o | Output directory. The default is "combineTree". |
| --mr | Majority rule trees.. |
| --mre | Extended majority rule trees. |
| --strict | Strict consensus trees. |
| --supertree | Use Spr_Supertree combining conflicting evolutionary histories that are due to lateral gene transfer (LGT). |
PhySpeTree provides the iview module to annotate taxonomic information (kingdom, phylum, class, or order) of output trees and to generate configure files linked to iTol.
Use iview in command line like this:
$ PhySpeTree iview -i organism_example_list.txt --range| -h | Print help message and exits. |
| -i | Input a TXT file containing abbreviated species names. |
| -o | A directory to store outputs. The default is "iview". |
| -r | Annotating labels with ranges by kingdom, phylum, class or order. The default is phylum. |
| -c | Annotating labels without ranges by kingdom, phylum, class or order. The default is phylum. |
| -a | Colored ranges by users assign, users can choice from [kingdom, phylum, class and order]. |
| -l | Change species labels from abbreviated names to full names. |
The check module is used to check whether input organisms are in pre-built databases.
$ PhySpeTree check -i organism_example_list.txt -out check --ehcp| -h | Print help message and exits. |
| -i | Input a TXT file containing abbreviated species names. |
| -o | A directory to store outputs. The default is "check". |
| --hcp | Check whether organisms are supported in the KEGG database. |
| --ehcp | Check input organisms prepare for extend autobuild tree module. |
| --srna | Check whether organisms are supported in the SILVA database. |
1.What is the input of PhySpeTree?
Users only need to prepare a TXT file containing KEGG abbreviated species names. For example, organism example list.
2.How to explain PhySpeTree outputs?
PhySpeTree returns two folders, Outdata contains the output species tree and temp includes temporary data. Files in temp can be used to check the quality of outputs in each step. If HCP method (--hcp) is selected, the temp folder includes:
- conserved_protein: highly conserved proteins retrieved from the KEGG database.
- alignment: aligned sequences.
- concatenate: concatenated sequences and conserved blocks.
If SSU rRNA method (--srna) is selected, the temp folder includes:
- rna_sequence: SSU rRNA sequences retrieved from the SILVA database.
- rna_alignment: aligned sequences and conserved blocks.
3.What classes of HCP are selected?
PhySpeTree uses 31 HCP without horizontal transferred genes according to Ciccarelli et al..
cite:
Ciccarelli F D, Doerks T, Von Mering C, et al. Toward automatic reconstruction of a highly resolved tree of life[J]. science, 2006, 311(5765): 1283-1287.
The 31 HCP and corresponding KEGG KO number are shown in the following table:
| Protein Names | Eukaryotes KO | Prokaryotes KO |
|---|---|---|
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit alpha | K03040 | K03040 |
| Ribosomal protein L1 | K02865 | K02863 |
| Leucyl-tRNA synthetase | K01869 | K01869 |
| Metal-dependent proteases with chaperone activity | K01409 | K01409 |
| Phenylalanine-tRNA synthethase alpha subunit | K01889 | K01889 |
| Predicted GTPase probable translation factor | K06942 | K06942 |
| Preprotein translocase subunit SecY | K10956 | K10956 |
| Ribosomal protein L11 | K02868 | K02867 |
| Ribosomal protein L13 | K02873 | K02871 |
| Ribosomal protein L14 | K02875 | K02874 |
| Ribosomal protein L15 | K02877 | K17437 |
| Ribosomal protein L16/L10E | K02866 | K02872 |
| Ribosomal protein L18 | K02883 | K02882 |
| Ribosomal protein L22 | K02891 | K02890 |
| Ribosomal protein L3 | K02925 | K02906 |
| Ribosomal protein L5 | K02932 | K02931 |
| Ribosomal protein L6P/L9E | K02940 | K02939 |
| Ribosomal protein S11 | K02949 | K02948 |
| Ribosomal protein S15P/S13E | K02958 | K02956 |
| Ribosomal protein S17 | K02962 | K02961 |
| Ribosomal protein S2 | K02981 | K02967 |
| Ribosomal protein S3 | K02985 | K02982 |
| Ribosomal protein S4 | K02987 | K02986 |
| Ribosomal protein S5 | K02989 | K02988 |
| Ribosomal protein S7 | K02993 | K02992 |
| Ribosomal protein S8 | K02995 | K02994 |
| Ribosomal protein S9 | K02997 | K02996 |
| Seryl-tRNA synthetase | K01875 | K01875 |
| Arginyl-tRNA synthetase | K01887 | K01887 |
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase beta subunit | K03043 | K03043 |
| Ribosomal protein S13 | K02953 | K02952 |
4.How are SSU rRAN created?
The SSU rRAN sequences are created from the SILVA database (123.1 release). Sequences haven been truncated, which means unaligned nucleotides are removed.
5. How do I use PhySpeTree when I can't connect to the Internet?
When users can't connect to the Internet. They can download the HCP or SSU rRNA database to local and reconstruct species tree.
- SSU rRNA database: database16s.tar.gz
- HCP database: databasehcp.tar.gz
Use $ tar -zxvf database16s.tar.gz decompress the download database.
Use -db option setting the absolute path to decompression directory.