npm i state-db.jsimport DB from 'state-db.js';
const db = new DB();可以通过schema字段限制字段的类型和是否必填
db.createTable({
name: 'articals', //required
schema: {
id: {type: 'Number', reuqired: true}
title: {type: 'String', required: true},
content: {type: 'String', required: false},
}, //options
initValue:[{id: 1, title: "我的奋斗", content: "你好。。。"}], //options
pramaryKey: "id" //options
})const articalTable = db.table('artical');需要注意的是,drop和clear只是在库中删除表,但是如果表对象依然被应用引用,表对象实际在内存中并未被清空
db.drop('artical'); //删除名为artical的表
db.clear(); //清除全部表db.bindFn((changeInfo) => {
console.log(changeInfo);
})articalTable.bindFn((changeInfo) => {
console.log(changeInfo);
})articalTable.insert({ id: 2, name: "hi,你好"});
articalTable.insert([
{id: 3, name: '21天精通C++'},
{id: 4,name: '21天精通Java'}
])articalTable.where('line.name=="我的奋斗"').delete()将查到的第一个值update
articalTable.where('line.id==1').update({name: "你的奋斗"});将查到的全部值update成同一个值
articalTable.where('line.id==1').updateAll({name: "你的奋斗"});传入一个数组 和 一个key值,当遇到key值相等的行时进行update
articalTable.updateByKey([{ id: 2, name: '奥特曼大战变形金刚' }, {id: 3, name: 'lee',}], 'id');注意:where语句由于底层使用了eval,对性能有影响,因此在循环中需要慎用,可以使用eq, filter, in等语句进行代替。
//指定条件的值
//getValues()保证每次取出的都是全新的对象,values则会使用缓存,和上次同一个查询使用同样的对象,使用values性能更好,使用getValues()更安全。
//只要进行过增删改操作,缓存都会清空。
articalTable.where('line.name=="我的奋斗 && index !== 1"').getValues(); //值是原值,后续操作不安全,仅能用于展示
articalTable.where('line.name=="我的奋斗 && index !== 1"').values; //值是原值,后续操作不安全,仅能用于展示
articalTable.where('line.name=="我的奋斗 && index !== 1"').getValues('safe'); //值是深copy出来的,后续操作是安全的。
//查前三个
articalTable.first(3).getValues();
//查后三个
articalTable.last(3).getValues();
//查name === "我的奋斗"
articalTable.eq('name', "我的奋斗").getValues();
//查id >= 3 && age <= 10
articalTable.filter('id', ">=", 3).filter('age', "<=", 10).getValues();
//查name=='test1' or name=='test3'
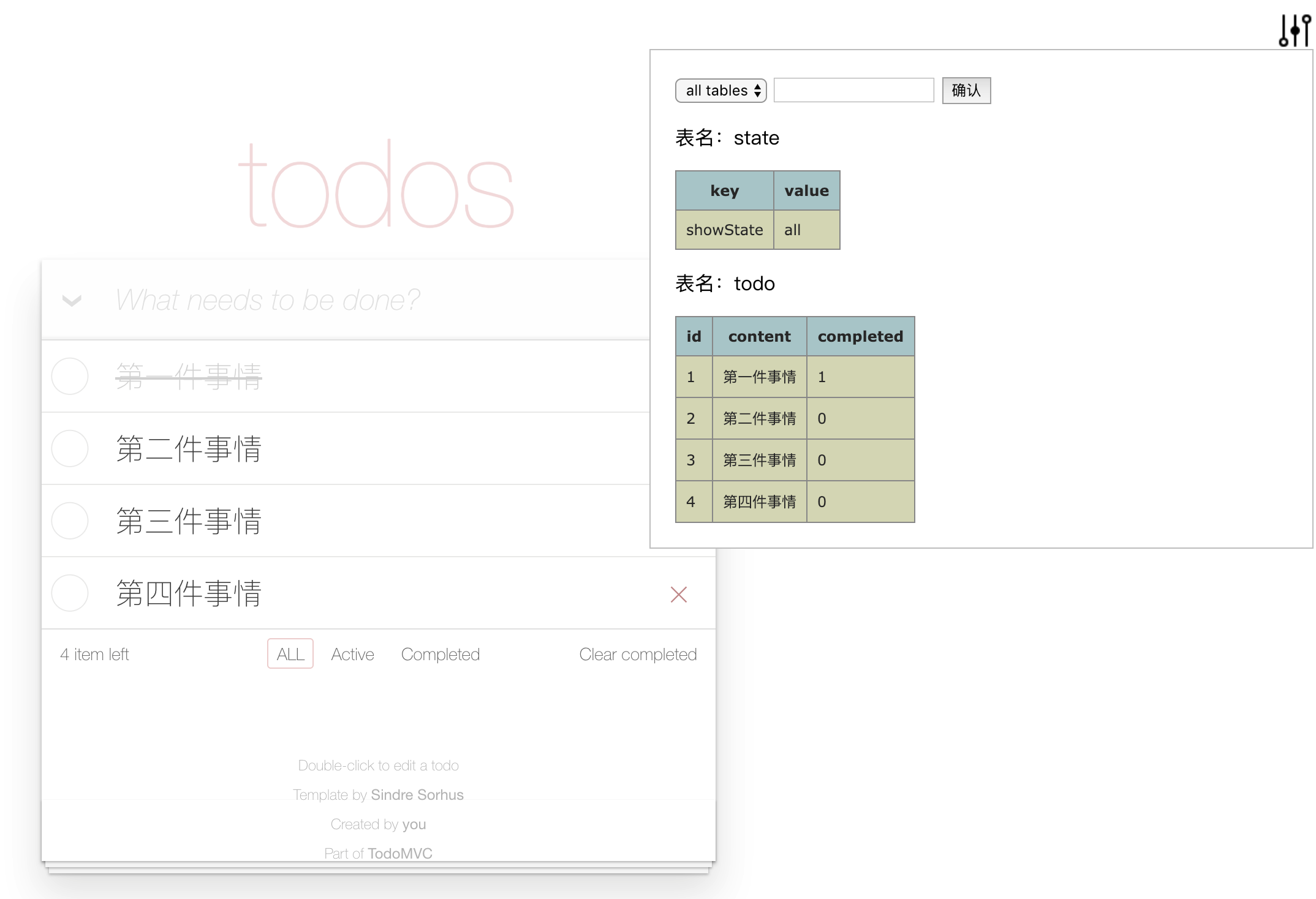
var arr = test1Table.in('name', ['test1', 'test3']).getValues();因为DB是非常结构化的并且能够反映全局的,可以有一个完整的视图来告知我们页面当前的状态,方便我们开发和debug。
import DB from 'state-db.js';
import devtool from 'state-db.js/build/devtool.bundle.esm.js'; //引入devtool
const db = new DB();
devtool(db, 'html', {hide: true}); //第二个参数默认为console
export default db;const getArticals = articalTable.getValues();
const render = () => {
str = `<ul>
${getArticals().map(artical => `<li>${artical.title}/</li>`)}
</ul>`
$('#app').innerHTML = str;
}
articalTable.bindFn(render);const getArticals = articalTable.getValues()
@db.dbconnectReact('artical')
class Artical extends Component {
render() {
return (<ul>
{getArticals().map(artical => <li>{artical.title}/</li>)
</ul>)
}
}const getArticals = articalTable.getValues()
new Vue({
mixins: [db.dbconnectVue('artical')],
//... your own logic
})
//全局模式,
//不传参数表示监听所有表(在mixin之前)
Vue.mixin(db.dbconnectVue())import DB from 'state-db.js';
import devtool from 'state-db.js/build/devtool.bundle.esm.js';
const db = new DB();
devtool(db, 'html'); //第二个参数默认为console
export default db;import db from '../db.js' //刚才已经new好的DB实例
db.createTable({name: 'configList'});
const configTable = db.table('configList');
const fetchConfigList = () => {
$.ajax({
url: url,
success: (res) => {configTable.init(res.data); }
})
}
const getConfig = (confName) => {
var arr = configTable.where('line.name == "'+ confName +'"').getValues;
if (arr.length) {
return arr[0].value;
}
else{
return none;
}
}
export {fetchConfigList, getConfig}step3.2: 对于某个路由或组件下独有的状态,比如一块独立的业务逻辑, 这时我们的建表语句和操作方法定义要放在组件的执行阶段 ,可以把model包装为一个函数,在组件入口执行处进行调用。db.dbconnectReact('todos')高阶组件会帮你进行组件和表之间的绑定和解绑。
import db from '../db.js'
const model = () => {
db.todoTable({name: 'todos' });
const todoTable = db.table('todos');
const fetchTodos = () => {
$.ajax({
url: url,
success: (res) => {todoTable.init(res.data);}
})
}
const getTodos = () => todoTable.getValues();
return { fetchTodos, getTodos}
}
@db.dbconnectReact('todos')
class Todo extends Component {
constructor() {
this.model = model();
}
componentDidMount(){
this.model.fetchTodos();
}
render() {
return(
return (<ul>
{this.model.getTodos().map(todo => <li>{todo.content}/</li>)
</ul>)
)
}
}